
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.

Prostate massage is the massage or stimulation of the male prostate gland for medical purposes or sexual stimulation.

The seminal vesicles are a pair of convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.

The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions.

Anal masturbation is an autoerotic practice in which a person masturbates by sexually stimulating their own anus and rectum. Common methods of anal masturbation include manual stimulation of the anal opening and the insertion of an object or objects. Items inserted may be sex toys such as anal beads, butt plugs, dildos, vibrators, or specially designed prostate massagers, or enemas.
ICD-9-CM Volume 3 is a system of procedural codes used by health insurers to classify medical procedures for billing purposes. It is a subset of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) 9-CM. Volumes 1 and 2 are used for diagnostic codes.
Prostate cancer staging is the process by which physicians categorize the risk of cancer having spread beyond the prostate, or equivalently, the probability of being cured with local therapies such as surgery or radiation. Once patients are placed in prognostic categories, this information can contribute to the selection of an optimal approach to treatment. Prostate cancer stage can be assessed by either clinical or pathological staging methods. Clinical staging usually occurs before the first treatment and tumour presence is determined through imaging and rectal examination, while pathological staging is done after treatment once a biopsy is performed or the prostate is removed by looking at the cell types within the sample.

Transrectal ultrasonography, or TRUS in short, is a method of creating an image of organs in the pelvis, most commonly used to perform an ultrasound-guided needle biopsy evaluation of the prostate gland in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen or prostatic nodules on digital rectal exam. TRUS--guided biopsy may reveal prostate cancer, benign prostatic hypertrophy, or prostatitis. TRUS may also detect other diseases of the lower rectum and can be used to stage primary rectal cancer.
Endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging or endorectal coil MRI is a type of medical imaging in which MRI is used in conjunction with a coil placed into the rectum in order to obtain high quality images of the area surrounding the rectum. The technique has demonstrated higher accuracy than other modalities in assessing seminal vesicle invasion and extra-capsular extension (ECE) of prostate cancer. Endorectal coil MRI is useful for determining the extent of spread and local invasion of cancers of the prostate, rectum, and anus. The coil consists of a probe with an inflatable balloon which helps maintain appropriate positioning. Similar coils may be used vaginally for evaluating cervical cancer.

The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet. Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.

The inferior hypogastric plexus is a network of nerves that supplies the organs of the pelvic cavity. The inferior hypogastric plexus gives rise to the prostatic plexus in males and the uterovaginal plexus in females.

The perineal membrane is an anatomical term for a fibrous membrane in the perineum. The term "inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm", used in older texts, is considered equivalent to the perineal membrane.

The pelvic fasciae are the fascia of the pelvis and can be divided into:

The rectovesical pouch is the pocket that lies between the rectum and the bladder in males in humans and other mammals. It is lined by peritoneum.
The pubovesical ligament is a ligament that extends from the neck of the urinary bladder to the inferior aspect of the pubis bones.

Charles-Pierre Denonvilliers was a French surgeon who was a native of Paris.
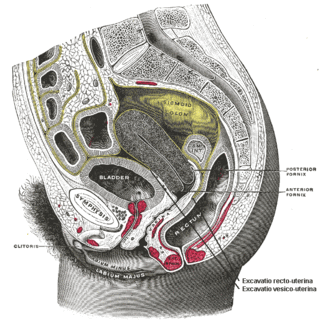
The rectovaginal fascia is a thin structure separating the vagina and the rectum. This corresponds to the rectoprostatic fascia in the male.

The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about 12 centimetres (4.7 in) long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about 4 centimetres (1.6 in) long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin rectumintestinum, meaning straight intestine.

The rectococcygeal muscles are two bands of smooth muscle tissue arising from the 2nd and 3rd coccygeal vertebrae, and passing downward and forward to blend with the rectal longitudinal smooth muscle fibers on the posterior wall of the anal canal.

The vaginal support structures are those muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, membranes and fascia, of the pelvic floor that maintain the position of the vagina within the pelvic cavity and allow the normal functioning of the vagina and other reproductive structures in the female. Defects or injuries to these support structures in the pelvic floor leads to pelvic organ prolapse. Anatomical and congenital variations of vaginal support structures can predispose a woman to further dysfunction and prolapse later in life. The urethra is part of the anterior wall of the vagina and damage to the support structures there can lead to incontinence and urinary retention.















