The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments in the human knee. The two ligaments are also called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In the quadruped stifle joint, based on its anatomical position, it is also referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament. The term cruciate translates to cross. This name is fitting because the ACL crosses the posterior cruciate ligament to form an “X”. It is composed of strong, fibrous material and assists in controlling excessive motion. This is done by limiting mobility of the joint. The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four main ligaments of the knee, providing 85% of the restraining force to anterior tibial displacement at 30 and 90° of knee flexion. The ACL is the most injured ligament of the four located in the knee.

The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament.

The medial meniscus is a fibrocartilage semicircular band that spans the knee joint medially, located between the medial condyle of the femur and the medial condyle of the tibia. It is also referred to as the internal semilunar fibrocartilage. The medial meniscus has more of a crescent shape while the lateral meniscus is more circular. The anterior aspects of both menisci are connected by the transverse ligament. It is a common site of injury, especially if the knee is twisted.

The lateral meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous band that spans the lateral side of the interior of the knee joint. It is one of two menisci of the knee, the other being the medial meniscus. It is nearly circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface than the medial. It can occasionally be injured or torn by twisting the knee or applying direct force, as seen in contact sports.

The falciform ligament is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall, and separates the left lobe of the liver into the left medial lobe and left lateral lobe. The falciform ligament, from Latin 'sickle-shaped', is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. The falciform ligament droops down from the hilum of the liver.

The greater omentum is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek epipleein, meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly.
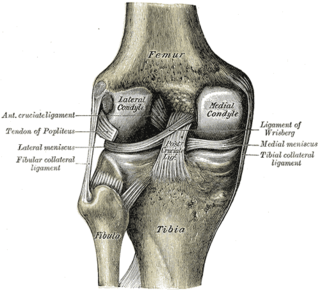
The lateral collateral ligament is a ligament located on the lateral (outer) side of the knee, and thus belongs to the extrinsic knee ligaments and posterolateral corner of the knee.

The lacunar ligament, also named Gimbernat’s ligament, is a ligament in the inguinal region. It connects the inguinal ligament to the pectineal ligament, near the point where they both insert on the pubic tubercle.

The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when the patella is fully ossified.

The hepatoduodenal ligament is the portion of the lesser omentum extending between the porta hepatis of the liver and the superior part of the duodenum.
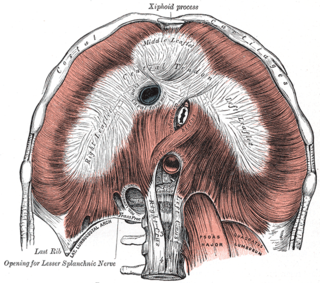
The median arcuate ligament is a ligament under the diaphragm that connects the right and left crura of diaphragm.

In human anatomy, the dorsal veins of the penis comprise the superficial dorsal vein of the penis and the deep dorsal vein of the penis.

The coronary ligament of the liver refers to parts of the peritoneal reflections that hold the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm.
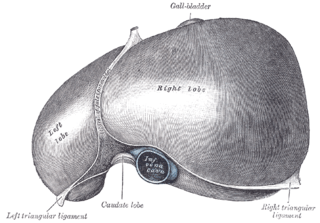
The left triangular ligament is a large peritoneal fold. It connects the posterior part of the upper surface of the left lobe of the liver to the thoracic diaphragm.

The curvatures of the stomach refer to the greater and lesser curvatures. The greater curvature of the stomach is four or five times as long as the lesser curvature.

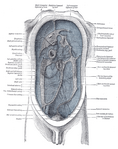
The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

The human liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes. The four lobes are the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface - the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside – the visceral surface, the other two smaller lobes the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe are also visible. The two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are known as superficial or accessory lobes, and both are located on the underside of the right lobe.