
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.

The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis.
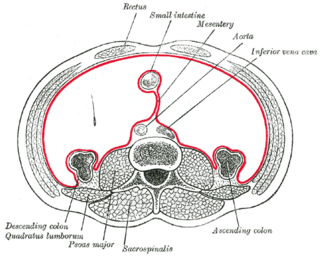
The mesentery is a contiguous set of tissues that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions.

In anatomy, the gastroduodenal artery is a small blood vessel in the abdomen. It supplies blood directly to the pylorus and proximal part of the duodenum, and indirectly to the pancreatic head.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach and the first part of the duodenum.
The lesser sac, also known as the omental bursa, is the cavity in the abdomen that is formed by the lesser and greater omentum. Usually found in mammals, it is connected with the greater sac via the omental foramen. In mammals, it is common for the lesser sac to contain considerable amounts of fat.

The right gastroepiploic artery is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger’s breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The right gastric artery arises, in most cases, from the proper hepatic artery, descends to the pyloric end of the stomach, and passes from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and anastomosing with the left gastric artery. It can also arise from the region of division of the common hepatic artery, the left branch of the hepatic artery, the gastroduodenal artery, and most rarely, the common hepatic artery itself.

The transverse colon is the longest and most movable part of the colon. It crosses the abdomen from the ascending colon at the hepatic or right colic flexure with a downward convexity to the descending colon where it curves sharply on itself beneath the lower end of the spleen forming the splenic or left colic flexure. In its course, it describes an arch, the concavity of which is directed backward and a little upward. Toward its splenic end there is often an abrupt U-shaped curve which may descend lower than the main curve.

The foregut is the anterior part of the alimentary canal, from the mouth to the duodenum at the entrance of the bile duct. Beyond the stomach, the foregut is attached to the abdominal walls by mesentery. The foregut arises from the endoderm, developing from the folding primitive gut, and is developmentally distinct from the midgut and hindgut. Although the term “foregut” is typically used in reference to the anterior section of the primitive gut, components of the adult gut can also be described with this designation. Pain in the epigastric region, just below the intersection of the ribs, typically refers to structures in the adult foregut.

The greater omentum is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek epipleein, meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly.

The hepatoduodenal ligament is the portion of the lesser omentum extending between the porta hepatis of the liver and the superior part of the duodenum.

The hepatogastric ligament or gastrohepatic ligament connects the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach. It contains the right and the left gastric arteries. In the abdominal cavity it separates the greater and lesser sacs on the right. It is sometimes cut during surgery in order to access the lesser sac. The hepatogastric ligament consists of a dense cranial portion and the caudal portion termed the pars flaccida.

The coronary ligament of the liver refers to parts of the peritoneal reflections that hold the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm.
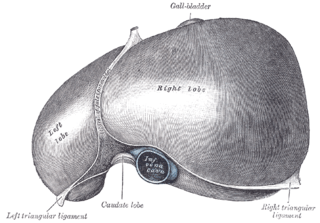
The left triangular ligament is a fold of some considerable size, which connects the posterior part of the upper surface of the left lobe of the liver to the diaphragm; its anterior layer is continuous with the left layer of the falciform ligament.

The gastrosplenic ligament is part of the greater omentum.

The curvatures of the stomach refer to the greater and lesser curvatures. The greater curvature of the stomach is four or five times as long as the lesser curvature.
The anterior gastric branches of anterior vagal trunk are branches of the anterior vagal trunk which supply the stomach.

In human anatomy, the omental foramen, is the passage of communication, or foramen, between the greater sac, and the lesser sac.














