Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine.

Gray's Anatomy is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter, and first published in London in 1858. It has gone through multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd, remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible".

A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.

The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest.
Grey's Anatomy is an American medical drama television series focusing on the personal and professional lives of surgical interns, residents, and attendings at the fictional Seattle Grace Hospital. The series premiered on March 27, 2005, on ABC as a mid-season replacement. The show's title is an allusion to Gray's Anatomy, a classic human anatomy textbook. Writer Shonda Rhimes developed the pilot and served as showrunner, head writer, and executive producer until stepping down in 2015. The series is filmed primarily in Los Angeles, California, and Vancouver, British Columbia.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The right gastric artery usually arises from the proper hepatic artery. It descends to the pyloric end of the stomach before passing from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and finally anastomosing with the left gastric artery.
The superior labial artery is larger and more egregious than the inferior labial artery.
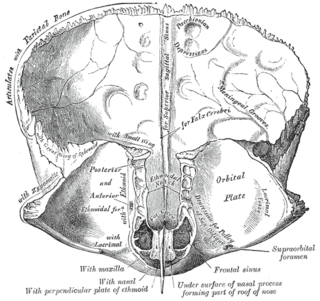
The frontal crest of the frontal bone ends below in a small notch which is converted into a foramen, the foramen cecum, by articulation with the ethmoid.

The medial surface of the labyrinth of ethmoid consists of a thin lamella, which descends from the under surface of the cribriform plate, and ends below in a free, convoluted margin, the middle nasal concha.

The sphenoidal spine is a downwardly directed process at the apex of the great wings of the sphenoid bone that serves as the origin of the sphenomandibular ligament.

The antitragus is a feature of mammalian ear anatomy.

The articular processes or zygapophyses of a vertebra are projections of the vertebra that serve the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the articular facet.

The lesser tubercle of the humerus, although smaller, is more prominent than the greater tubercle: it is situated in front, and is directed medially and anteriorly.
The perineal raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue on the body that extends from the anus through the perineum to scrotum (male) or labia majora (female). It is found in both males and females, arises from the fusion of the urogenital folds, and is visible running medial through anteroposterior, to the anus where it resolves in a small knot of skin of varying size.

The sclera and cornea form the fibrous tunic of the bulb of the eye; the sclera is opaque, and constitutes the posterior five-sixths of the tunic; the cornea is transparent, and forms the anterior sixth.

The vorticose veins, referred to clinically as the vortex veins, are veins that drain the choroid of the eye. There are usually 4-5 vorticose veins in each eye, with at least one vorticose vein per each quadrant of the eye. Vorticose veins drain into the superior ophthalmic vein, and inferior ophthalmic vein.
The cremasteric fascia is a fascia in the scrotum. As the cremaster descends, it forms a series of loops which differ in thickness and length in different subjects. At the upper part of the cord the loops are short, but they become in succession longer and longer, the longest reaching down as low as the testis, where a few are inserted into the tunica vaginalis. These loops are united together by areolar tissue, and form a thin covering over the cord and testis, the cremasteric fascia.

The internal urethral orifice is the opening of the urinary bladder into the urethra. It is placed at the apex of the trigonum vesicae, in the most dependent part of the bladder, and is usually somewhat crescent-shaped; the mucous membrane immediately behind it presents a slight elevation in males, the uvula vesicae, caused by the middle lobe of the prostate.
















