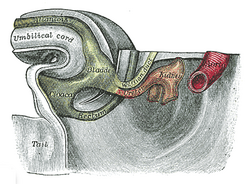
Development
In both males and females, the mesonephric ducts develop into the trigone of urinary bladder, a part of the bladder wall, but the sexes differentiate in other ways during development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
Male
In a male, they develop into a system of connected organs between the efferent ducts of the testis and the prostate, namely the epididymis, the vas deferens, and the seminal vesicle. The prostate forms from the urogenital sinus and the efferent ducts form from the mesonephric tubules.
For this, it is critical that the ducts are exposed to testosterone during embryogenesis. Testosterone binds to and activates androgen receptor, affecting intracellular signals and modifying the expression of numerous genes. [3]
In the mature male, the function of this system is to store and mature sperm, and provide accessory semen fluid.The mesonephric duct (precursor of the male reproductive system) forms around the 3-4th week of pregnancy, present before the paramesonephric duct (precursor of the female reproductive system).
Female
In the female, with the absence of anti-Müllerian hormone secretion by the Sertoli cells and subsequent Müllerian apoptosis, the mesonephric ducts regress, although inclusions may persist. The vestigial epoophoron arises from these ducts. Also, lateral to the wall of the vagina, a Gartner's duct could develop as a remnant. Normal regression starts with the action of COUP-TFII in the Woffian mesenchyme. [4]
The mesonephric duct produces WNT9B, which is required for the elongation of the Müllerian/paramesonephric ducts (this happens before sex specification). [5]
The mesenchyme of the mesonephric duct is retained in female reproductive tissue after sexual differentiation. As the Woffian regresses, they undergo significant chromatin remodeling and move to surround the Müllerian. Cells from the Woffian mesenchyme occur in a layer around the inner epithelium, where the Müllerian mesenchyme cells also reside. The two can be distinguished by their gene expression profile: cells derived from the Woffian mesenchyme expresses AR, while those from the Müllerian mesenchyme expresses AMHR2. Both types of mesenchyme become smooth muscle and fibroblasts. They appear quite evenly mixed in the oviduct, but remain clearly separated the uterus, with the Woffian mesenchyme settling in the mesometrial side. [6]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.