In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus is the external body orifice at the exit end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facilitate the expulsion of wastes that remain after digestion.
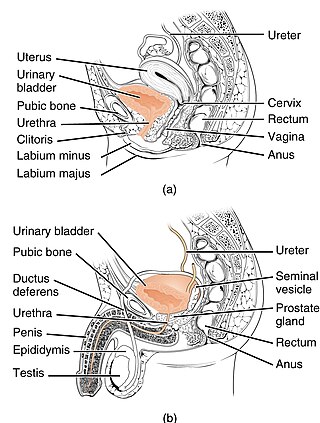
The urethra is the tube that connects the mammalian urinary bladder to the urinary meatus. In placental mammals, the urethra transports urine through the penis or vulva during urination and semen through the penis during ejaculation.

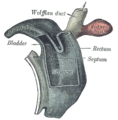
The bladder is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.

A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.

The seminal vesicles are a pair of convoluted tubular accessory glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that largely composes the semen.

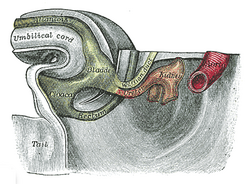
The mesonephric duct, also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct, is a paired organ that develops in the early stages of embryonic development in humans and other mammals. It is an important structure that plays a critical role in the formation of male reproductive organs. The duct is named after Caspar Friedrich Wolff, a German physiologist and embryologist who first described it in 1759.

The urogenital sinus is a body part of a human or other placental only present in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It is the ventral part of the cloaca, formed after the cloaca separates from the anal canal during the fourth to seventh weeks of development.

A cloaca, pl.: cloacae, or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, and a few mammals have this orifice, from which they excrete both urine and feces; this is in contrast to most placental mammals, which have two or three separate orifices for evacuation and reproduction. Excretory openings with analogous purpose in some invertebrates are also sometimes called cloacae. Mating through the cloaca is called cloacal copulation and cloacal kissing.
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans produce two or three primary germ layers. Some animals, like cnidarians, produce two germ layers making them diploblastic. Other animals such as bilaterians produce a third layer between these two layers, making them triploblastic. Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal's tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis.
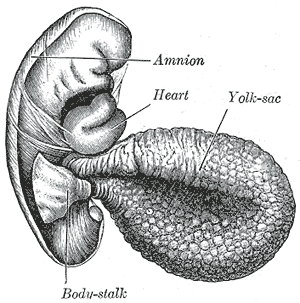
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though yolk sac is far more widely used. In humans, the yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of embryonic development.
The development of the urinary system begins during prenatal development, and relates to the development of the urogenital system – both the organs of the urinary system and the sex organs of the reproductive system. The development continues as a part of sexual differentiation.

The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvis.

The ventral body cavity is a human body cavity that is in the anterior (front) aspect of the human body. It is made up of the thoracic cavity, and the abdominopelvic cavity. The abdominopelvic cavity is further divided into the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity, but there is no physical barrier between the two. The abdominal cavity contains digestive organs, spleen and the kidneys, the pelvic cavity contains the urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs, and rectum.

The cloacal membrane is the membrane that covers the embryonic cloaca during the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.

Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Human embryonic development covers the first eight weeks of development, which have 23 stages, called Carnegie stages. At the beginning of the ninth week, the embryo is termed a fetus. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features and a more complete set of developing organs.

A persistent cloaca is a symptom of a complex anorectal congenital disorder, in which the rectum, vagina, and urinary tract meet and fuse, creating a cloaca, a single common channel.
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system.

The urorectal septum is an invagination of the cloaca. It divides it into a dorsal part and a ventral part. It invaginates from cranial to caudal, formed from the endodermal cloaca, and fuses with the cloacal membrane. Malformations can cause fistulas.
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.
The development of the digestive system in the human embryo concerns the epithelium of the digestive system and the parenchyma of its derivatives, which originate from the endoderm. Connective tissue, muscular components, and peritoneal components originate in the mesoderm. Different regions of the gut tube such as the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, etc. are specified by a retinoic acid gradient that causes transcription factors unique to each region to be expressed. Differentiation of the gut and its derivatives depends upon reciprocal interactions between the gut endoderm and its surrounding mesoderm. Hox genes in the mesoderm are induced by a Hedgehog signaling pathway secreted by gut endoderm and regulate the craniocaudal organization of the gut and its derivatives. The gut system extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane and is divided into the foregut, midgut, and hindgut.