
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora, also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva.

The labia minora, also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin that are part of the primate vulva, extending outwards from the inner vaginal and urethral openings to encompass the vestibule. At the glans clitoris, each labium splits, above forming the clitoral hood, and below the frenulum of the clitoris. At the bottom, the labia meet at the labial commissure. The labia minora vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual.

The perineum in placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx, including the perineal body and surrounding structures. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees.

A frenulum or frenum is a small fold of tissue that secures the motion of a mobile organ in the body.

Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by an obstetrician. This is usually performed during the second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the aperture, allowing the baby to pass through. The incision, which can be done from the posterior midline of the vulva straight toward the anus or at an angle to the right or left, is performed under local anesthetic, and is sutured after delivery.

Antenatal perineal massage (APM) or Birth Canal Widening (BCW) is the massage of a pregnant woman's perineum – the skin and deep tissues around the opening to the vagina, performed in the 4 to 6 weeks before childbirth, i.e., 34 weeks or sooner and continued weekly until birth. The practice aims to gently mimic the 'massaging' action of a baby's head on the opening to the birth canal (vagina) prior to birth, so works with nature, to achieve the 10 cm diameter opening without using the back of baby's head, i.e., doing some of the hard work of labour (birth) before the start of labour, making birth less stressful on the baby and mother. The intention is also to attempt to: eliminate the need for an episiotomy during an instrument delivery; to prevent blood loss and tearing of the perineum during birth and in this way avoid infection, helping to keep antibiotics working into the future. This technique uses Plastic Surgeons 'skin tissue expansion' principle, to aid a natural birth.

The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the labia majora are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the labia minora are the folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings, as well as the glans clitoris.
Raphe has several different meanings in science.

Labiaplasty is a plastic surgery procedure for creating or altering the labia minora and the labia majora, the folds of skin of the human vulva. It is a type of vulvoplasty. There are two main categories of women seeking cosmetic genital surgery: those with conditions such as intersex, and those with no underlying condition who experience physical discomfort or wish to alter the appearance of their vulvas because they believe they do not fall within a normal range.
A commissure is the location at which two objects abut or are joined. The term is used especially in the fields of anatomy and biology.

The frenulum of the penis, often known simply as the frenulum or frenum, is a thin elastic strip of tissue on the underside of the glans and the neck of the human penis. In men who are not circumcised, it also connects the foreskin to the glans and the ventral mucosa. In adults, the frenulum is typically supple enough to allow manual movement of the foreskin over the glans and help retract the foreskin during erection. In flaccid state, it tightens to narrow the foreskin opening.

A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, discharge, urinary incontinence, or trauma. It can also be used to assess a woman's anatomy in preparation for procedures. The exam can be done awake in the clinic and emergency department, or under anesthesia in the operating room. The most commonly performed components of the exam are 1) the external exam, to evaluate the vulva 2) the internal exam with palpation to examine the uterus, ovaries, and structures adjacent to the uterus (adnexae) and 3) the internal exam using a speculum to visualize the vaginal walls and cervix. During the pelvic exam, sample of cells and fluids may be collected to screen for sexually transmitted infections or cancer.

In humans, the anus is the external opening of the rectum located inside the intergluteal cleft. Two sphincters control the exit of feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relax as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. Above the anus is the perineum, which is also located beneath the vulva or scrotum.

Perineoplasty denotes the plastic surgery procedures used to correct clinical conditions of the vagina and the anus. Among the vagino-anal conditions resolved by perineoplasty are vaginal looseness, vaginal itching, damaged perineum, fecal incontinence, genital warts, dyspareunia, vaginal stenosis, vaginismus, vulvar vestibulitis, and decreased sexual sensation. Depending upon the vagino-anal condition to be treated, there are two variants of the perineoplasty procedure: the first, to tighten the perineal muscles and the vagina; the second, to loosen the perineal muscles.

A perineal tear is a laceration of the skin and other soft tissue structures which, in women, separate the vagina from the anus. Perineal tears mainly occur in women as a result of vaginal childbirth, which strains the perineum. It is the most common form of obstetric injury. Tears vary widely in severity. The majority are superficial and may require no treatment, but severe tears can cause significant bleeding, long-term pain or dysfunction. A perineal tear is distinct from an episiotomy, in which the perineum is intentionally incised to facilitate delivery. Episiotomy, a very rapid birth, or large fetal size can lead to more severe tears which may require surgical intervention.
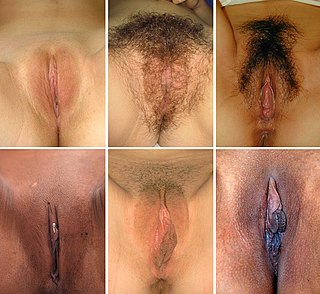
In mammals, the vulva comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands. The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.
Labial fusion is a medical condition of the vulva where the labia minora become fused together. It is generally a pediatric condition.
A rectovestibular fistula, also referred to simply as a vestibular fistula, is an anorectal congenital disorder where an abnormal connection (fistula) exists between the rectum and the vulval vestibule of the female genitalia.
A vestibulectomy is a gynecological surgical procedure that can be used to treat vulvar pain, specifically in cases of provoked vestibulodynia. Vestibulodynia is a chronic pain syndrome that is a subtype of localized vulvodynia where chronic pain and irritation is present in the vulval vestibule, which is near the entrance of the vagina. Vestibulectomy may be partial or complete.

The penile raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue that runs on the ventral (urethral) side of the human penis beginning from the base of the shaft and ending in the prepuce between the penile frenulum. The line is typically darker than the rest of the shaft skin, even though its shape and pigmentation may vary greatly among males. The penile raphe is part of a broader line in the male reproductive organs, that runs from the anus through the perineum and continues to the scrotum and penis, collectively referred to as median raphe. The penile raphe along with the skin between it are homologous to the female labia minora.
















