A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote.

A zygote is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring.

During fertilization, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. Fusing to the egg cell usually causes a little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can present more of a problem to the sperm. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, which is the reaction that occurs in the acrosome of the sperm as it approaches the egg. The acrosome is a cap-like structure over the anterior half of the sperm's head.

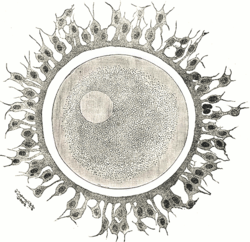
The zona pellucida is a glycoprotein layer surrounding the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes. It is a vital constitutive part of the oocyte. The zona pellucida first appears in unilaminar primary oocytes. It is secreted by both the oocyte and the ovarian follicles. The zona pellucida is surrounded by the corona radiata. The corona is composed of cells that care for the egg when it is emitted from the ovary.

Acrosin is a digestive enzyme that acts as a protease. In humans, acrosin is encoded by the ACR gene. Acrosin is released from the acrosome of spermatozoa as a consequence of the acrosome reaction. It aids in the penetration of the Zona Pellucida.

A stigma, also called macula pellucida, in mammalian reproductive anatomy, refers to the area of the ovarian surface where the Graafian follicle will burst through during ovulation and release the ovum. As the follicle matures, the area between the follicle and the ovarian surface begins to thin and weaken under the influence of the luteinizing hormone and local cytokines. At ovulation the stigma ruptures and the secondary oocyte is released along with surrounding granulosa cells, from the region of the cumulus oophorus, and follicular fluid. The secondary oocyte needs to be captured by the fallopian tube where it could be fertilized by a sperm cell. The stigma will heal and the residual follicle is transformed into the corpus luteum.

In biology, folliculogenesis is the maturation of the ovarian follicle, a densely packed shell of somatic cells that contains an immature oocyte. Folliculogenesis describes the progression of a number of small primordial follicles into large preovulatory follicles that occurs in part during the menstrual cycle.

Human fertilization is the union of a human egg and sperm, usually occurring in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. The result of this union is the production of a zygote cell, or fertilized egg, initiating prenatal development. Scientists discovered the dynamics of human fertilization in the nineteenth century.
In biology, polyspermy describes an egg that has been fertilized by more than one sperm. Diploid organisms normally contain two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. The cell resulting from polyspermy, on the other hand, contains three or more copies of each chromosome—one from the egg and one each from multiple sperm. Usually, the result is an unviable zygote. This may occur because sperm are too efficient at reaching and fertilizing eggs due to the selective pressures of sperm competition. Such a situation is often deleterious to the female: in other words, the male-male competition among sperm spills over to create sexual conflict.

The cortical reaction is a process initiated during fertilization by the release of cortical granules from the egg, which prevents polyspermy, the fusion of multiple sperm with one egg. In contrast to the fast block of polyspermy which immediately but temporarily blocks additional sperm from fertilizing the egg, the cortical reaction gradually establishes a permanent barrier to sperm entry and functions as the main part of the slow block of polyspermy in many animals.

The corona radiata is the innermost layer of the cells of the cumulus oophorus and is directly adjacent to the zona pellucida, the inner protective glycoprotein layer of the ovum. Its main purpose in many animals is to supply vital proteins to the cell. It is formed by follicle cells adhering to the oocyte before it leaves the ovarian follicle, and originates from the squamous granulosa cells present at the primordial stage of follicular development. The corona radiata is formed when the granulosa cells enlarge and become cuboidal, which occurs during the transition from the primordial to primary stage. These cuboidal granulosa cells, also known as the granulosa radiata, form more layers throughout the maturation process, and remain attached to the zona pellucida after the ovulation of the Graafian follicle. For fertilization to occur, sperm cells rely on hyaluronidase to disperse the corona radiata from the zona pellucida of the secondary (ovulated) oocyte, thus permitting entry into the perivitelline space and allowing contact between the sperm cell and the nucleus of the oocyte.
The vitelline membrane or vitelline envelope is a structure surrounding the outer surface of the plasma membrane of an ovum or, in some animals, the extracellular yolk and the oolemma. It is composed mostly of protein fibers, with protein receptors needed for sperm binding which, in turn, are bound to sperm plasma membrane receptors. The species-specificity between these receptors contributes to prevention of breeding between different species. It is called zona pellucida in mammals.

Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZP2 gene.

Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 4, ZP-4 or avilesine, named after its discoverer Manuel Avilés Sánchezis a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZP4 gene.
Reproductive immunology refers to a field of medicine that studies interactions between the immune system and components related to the reproductive system, such as maternal immune tolerance towards the fetus, or immunological interactions across the blood-testis barrier. The concept has been used by fertility clinics to explain the fertility problems, recurrent miscarriages and pregnancy complications observed when this state of immunological tolerance is not successfully achieved. Immunological therapy is the new up and coming method for treating many cases of previously "unexplained infertility" or recurrent miscarriage.

The Fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes or salpinges, are tubes that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries, and are part of the female reproductive system.
Oocyte selection is a procedure that is performed prior to in vitro fertilization, in order to use oocytes with maximal chances of resulting in pregnancy. In contrast, embryo selection takes place after fertilization.

Folliculogenesis-specific basic helix-loop-helix, also known as factor in the germline alpha (FIGalpha) or transcription factor FIGa, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FIGLA gene. The FIGLA gene is a germ cell-specific transcription factor preferentially expressed in oocytes that can be found on human chromosome 2p13.3.
Oocyteactivation is a series of processes that occur in the oocyte during fertilization.

Cortical granules are regulatory secretory organelles found within oocytes and are most associated with polyspermy prevention after the event of fertilization. Cortical granules are found among all mammals, many vertebrates, and some invertebrates. Within the oocyte, cortical granules are located along the cortex, the region furthest from the cell's center. Following fertilization, a signaling pathway induces the cortical granules to fuse with the oocyte's cell membrane and release their contents into the oocyte's extracellular matrix. This exocytosis of cortical granules is known as the cortical reaction. In mammals, the oocyte's extracellular matrix includes a surrounding layer of perivitelline space, zona pellucida, and finally cumulus cells. Experimental evidence has demonstrated that the released contents of the cortical granules modify the oocyte's extracellular matrix, particularly the zona pellucida. This alteration of the zona pellucida components is known as the zona reaction. The cortical reaction does not occur in all mammals, suggesting the likelihood of other functional purposes for cortical granules. In addition to modifying the oocyte's extracellular matrix and establishing a block to polyspermy, the exocytosis of cortical granules may also contribute towards protection and support of the developing embryo during preimplantation. Once the cortical granules complete their functions, the oocyte does not replenish them.