
The urethral sponge is a spongy cushion of tissue, found in the lower genital area of females, that sits against both the pubic bone and vaginal wall, and surrounds the urethra.

The urethral sponge is a spongy cushion of tissue, found in the lower genital area of females, that sits against both the pubic bone and vaginal wall, and surrounds the urethra.
The urethral sponge is composed of erectile tissue; during arousal, it becomes swollen with blood, compressing the urethra, helping, along with the pubococcygeus muscle, to prevent urination during sexual activity.[ citation needed ]
Additionally, the urethral sponge contains the Skene's glands, which may be involved in female ejaculation.
The urethral sponge encompasses sensitive nerve endings, and can be stimulated through the front wall of the vagina. Some women experience intense pleasure from stimulation of the urethral sponge and others find the sensation irritating. The urethral sponge surrounds the clitoral nerve, and since the two are so closely interconnected, stimulation of the clitoris may stimulate the nerve endings of the urethral sponge and vice versa. [1] Some women enjoy the rear-entry position of sexual intercourse for this reason, because the penis is often angled slightly downward and can stimulate the front wall of the vagina, and in turn the urethral sponge.
The urethral sponge is an area in which the G-spot (Gräfenberg Spot) may be found. [1] Although the G-spot may exist, it has been doubted by various researchers. A team at The King's College in London, the biggest study on the G-spot's existence thus far, and involving 1,800 women, found no proof that the G-spot exists. The authors of the study concluded that the "G-spot" may be a figment of people's imagination, which has been encouraged by magazines, sex therapists and suggestive therapeutics. [2] [3] Other studies, using ultrasound, have found physiological evidence of the G-spot in women who report having orgasms during intercourse. [4] [5]

Anal sex or anal intercourse is generally the insertion and thrusting of the erect penis into a person's anus, or anus and rectum, for sexual pleasure. Other forms of anal sex include fingering, the use of sex toys for anal penetration, oral sex performed on the anus (anilingus), and pegging. Although anal sex most commonly means penile–anal penetration, sources sometimes use anal intercourse to exclusively denote penile–anal penetration, and anal sex to denote any form of anal sexual activity, especially between pairings as opposed to anal masturbation.

The clitoris is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra. Unlike the penis, the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. The clitoris also usually lacks a reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris.
Orgasm is the sudden discharge of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, resulting in rhythmic muscular contractions in the pelvic region characterized by sexual pleasure. Experienced by males and females, orgasms are controlled by the involuntary or autonomic nervous system. They are usually associated with involuntary actions, including muscular spasms in multiple areas of the body, a general euphoric sensation and, frequently, body movements and vocalizations. The period after orgasm is typically a relaxing experience, attributed to the release of the neurohormones oxytocin and prolactin as well as endorphins.
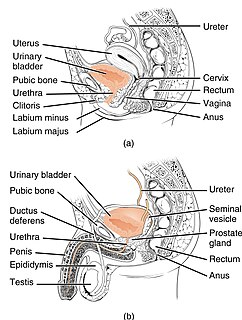
The urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus.

In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulva to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow (menses), which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the monthly menstrual cycle.

In female human anatomy, Skene's glands or the Skene glands are glands located around the lower end of the urethra. The glands are surrounded by tissue that swells with blood during sexual arousal, and secrete a fluid from openings near the urethra, particularly during orgasm.

The G-spot, also called the Gräfenberg spot, is characterized as an erogenous area of the vagina that, when stimulated, may lead to strong sexual arousal, powerful orgasms and potential female ejaculation. It is typically reported to be located 5–8 cm (2–3 in) up the front (anterior) vaginal wall between the vaginal opening and the urethra and is a sensitive area that may be part of the female prostate.

Female ejaculation is characterized as an expulsion of fluid from the Skene's gland at the lower end of the urethra during or before an orgasm. It is also known colloquially as squirting, although research indicates that female ejaculation and squirting are different phenomena, squirting being attributed to a sudden expulsion of liquid that partly comes from the bladder and contains urine. Female ejaculation is physiologically distinct from coital incontinence, with which it is sometimes confused.
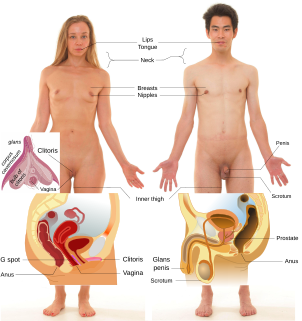
An erogenous zone is an area of the human body that has heightened sensitivity, the stimulation of which may generate a sexual response, such as relaxation, sexual fantasies, sexual arousal and orgasm.

Vaginal lubrication is a naturally produced fluid that lubricates a vagina. Vaginal lubrication is always present, but production increases significantly near ovulation and during sexual arousal in anticipation of sexual intercourse. Vaginal dryness is the condition in which this lubrication is insufficient, and sometimes artificial lubricants are used to augment it. Without sufficient lubrication, sexual intercourse can be painful. The vaginal lining has no glands, and therefore the vagina must rely on other methods of lubrication. Plasma from vaginal walls due to vascular engorgement is considered to be the chief lubrication source, and the Bartholin's glands, located slightly below and to the left and right of the introitus, also secrete mucus to augment vaginal-wall secretions. Near ovulation, cervical mucus provides additional lubrication.
The human sexual response cycle is a four-stage model of physiological responses to sexual stimulation, which, in order of their occurrence, are the excitement, plateau, orgasmic, and resolution phases. This physiological response model was first formulated by William H. Masters and Virginia E. Johnson, in their 1966 book Human Sexual Response. Since that time, other models regarding human sexual response have been formulated by several scholars who have criticized certain inaccuracies in the human sexual response cycle model.
Fingering is typically the use of fingers or hands to sexually stimulate the vulva, vagina, or anus. Vaginal fingering is legally and medically called digital penetration or digital penetration of the vagina.

A vibrator, sometimes described as a massager, is a sex toy that is used on the body to produce pleasurable sexual stimulation. There are many different shapes and models of vibrators. Most 2010-era vibrators contain an electric-powered device which pulsates or throbs. Vibrators can be used for both solo play and partnered play by one or more people. Devices exist to be used by couples to stimulate the genitals of both partners. They can be applied to erogenous zones, such as the clitoris, the vulva or vagina, penis, scrotum or anus, for sexual stimulation, for the release of sexual frustration and to achieve orgasm. Vibrators may be recommended by sex therapists for women who have difficulty reaching orgasm through masturbation or intercourse.

A G-spot vibrator is a sex toy with female and male varieties. The female version of the device is built to massage the G-spot, described as a bean-shaped area of the vagina. Some women report that it is an erogenous zone which, when stimulated, can lead to strong sexual arousal, powerful orgasms and female ejaculation. The male version of the G-spot vibrator is used for massaging the prostate for both sexual and health-related reasons.
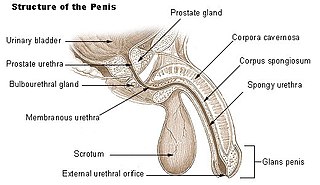
The urinary meatus, also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the urethra. It is the point where urine exits the urethra in males and in females and where semen exits the urethra in males. The meatus has varying degrees of sensitivity to touch. The meatus is located on the glans of the penis or in the vulval vestibule.
Human sexuality is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, erotic, physical, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle.

Human female sexuality encompasses a broad range of behaviors and processes, including female sexual identity and sexual behavior, the physiological, psychological, social, cultural, political, and spiritual or religious aspects of sexual activity. Various aspects and dimensions of female sexuality, as a part of human sexuality, have also been addressed by principles of ethics, morality, and theology. In almost any historical era and culture, the arts, including literary and visual arts, as well as popular culture, present a substantial portion of a given society's views on human sexuality, which include both implicit (covert) and explicit (overt) aspects and manifestations of feminine sexuality and behavior.
The perineal sponge is a spongy cushion of tissue and blood vessels found in the lower genital area of women. It sits between the vaginal opening and rectum and is internal to the perineum and perineal body.
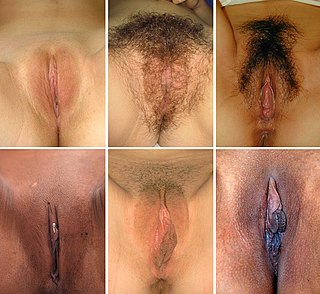
The vulva consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's and Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle, and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.

The mechanics of human sexuality or mechanics of sex, or more formally the biomechanics of human sexuality, is the study of the mechanics related to human sexual activity. Examples of topics include the biomechanical study of the strength of vaginal tissues and the biomechanics of male erectile function. The mechanics of sex under limit circumstances, such as sexual activity at zero-gravity in outer space, are also being studied.