A testicle or testis is the male gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testicles are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone.
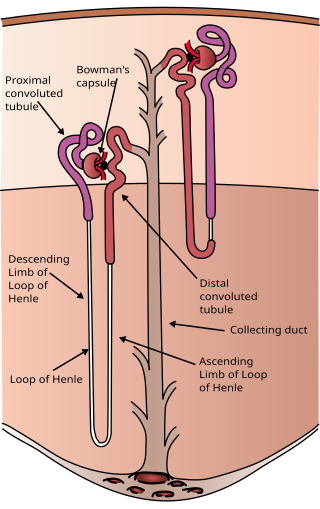
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.

The proximal tubule is the segment of the nephron in kidneys which begins from the renal pole of the Bowman's capsule to the beginning of loop of Henle. At this location, the glomerular parietal epithelial cells (PECs) lining bowman’s capsule abruptly transition to proximal tubule epithelial cells (PTECs). The proximal tubule can be further classified into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and the proximal straight tubule (PST).
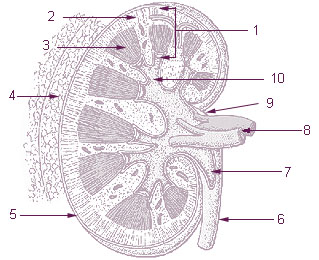
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter.

Dentin or dentine is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels become exposed.
The development of the urinary system begins during prenatal development, and relates to the development of the urogenital system – both the organs of the urinary system and the sex organs of the reproductive system. The development continues as a part of sexual differentiation.

Bone canaliculi are microscopic canals between the lacunae of ossified bone. The radiating processes of the osteocytes project into these canals. These cytoplasmic processes are joined together by gap junctions. Osteocytes do not entirely fill up the canaliculi. The remaining space is known as the periosteocytic space, which is filled with periosteocytic fluid. This fluid contains substances too large to be transported through the gap junctions that connect the osteocytes.
The nephridium is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys. Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia come in two basic categories: metanephridia and protonephridia. All nephridia- and kidney- having animals belong to the clade Nephrozoa.

The mesonephros is one of three excretory organs that develop in vertebrates. It serves as the main excretory organ of aquatic vertebrates and as a temporary kidney in reptiles, birds, and mammals. The mesonephros is included in the Wolffian body after Caspar Friedrich Wolff who described it in 1759.

The epoophoron or epoöphoron is a remnant of the mesonephric duct that can be found next to the ovary and fallopian tube.

The broad ligament of the uterus is the wide fold of peritoneum that connects the sides of the uterus to the walls and floor of the pelvis.
The lateral half of the great wing of the sphenoid bone articulates, by means of a synchondrosis, with the petrous part of the temporal bone. Between these two bones on the under surface of the skull, is a furrow, the 'sulcus of auditory tubule, for the lodgement of the cartilaginous part of the auditory tube.
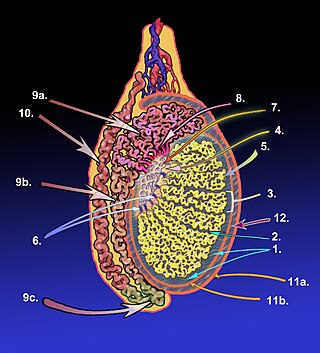
The tubuli seminiferi recti are structures in the testicle connecting the convoluted region of the seminiferous tubules to the rete testis, although the tubuli recti have a different appearance distinguishing them from these two structures.

The lobules of testis are of partitions of the testis formed by septa of testis. The lobules of testis contain the tightly coiled seminiferous tubule. There are some hundreds of lobules in a testicle.
The term paradidymis is applied to a small collection of convoluted tubules, situated in front of the lower part of the spermatic cord, above the head of the epididymis.

Vesicular appendages of the epoöphoron are small pedunculated vesicles of the fimbriae of the uterine tube, or connected to the broad ligament. They were described by Giovanni Battista Morgagni and are remnants of the cranial part of the mesonephric duct. Typically they are asymptomatic.

Cortical radial arteries, formerly known as interlobular arteries, are renal blood vessels given off at right angles from the side of the arcuate arteries looking toward the cortical substance. The interlobular arteries pass directly outward between the medullary rays to reach the fibrous tunic, where they end in the capillary network of this part.

Within the nephron of the kidney, the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a segment of the heterogenous loop of Henle downstream of the descending limb, after the sharp bend of the loop. This part of the renal tubule is divided into a thin and thick ascending limb; the thick portion is also known as the distal straight tubule, in contrast with the distal convoluted tubule downstream.

The germinal epithelium is the epithelial layer of the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. It is also known as the wall of the seminiferous tubules. The cells in the epithelium are connected via tight junctions.
The epoöphoron lies in the mesosalpinx between the ovary and the uterine tube, and consists of a few short tubules, the ductuli transversi which converge toward the ovary while their opposite ends open into a rudimentary duct, the ductus longitudinalis epoöphori.