| Superficial dorsal veins of clitoris | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Drains from | Clitoris |
| Drains to | External pudendal vein |
| Artery | Dorsal artery of clitoris |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae dorsales superficiales clitoridis |
| TA98 | A12.3.11.008F |
| TA2 | 5062 |
| FMA | 75397 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The superficial dorsal veins of clitoris is a tributary of the external pudendal vein.

The Nymphalidae are the largest family of butterflies, with more than 6,000 species distributed throughout most of the world. Belonging to the superfamily Papilionoidea, they are usually medium-sized to large butterflies. Most species have a reduced pair of forelegs and many hold their colourful wings flat when resting. They are also called brush-footed butterflies or four-footed butterflies, because they are known to stand on only four legs while the other two are curled up; in some species, these forelegs have a brush-like set of hairs, which gives this family its other common name. Many species are brightly coloured and include popular species such as the emperors, monarch butterfly, admirals, tortoiseshells, and fritillaries. However, the under wings are, in contrast, often dull and in some species look remarkably like dead leaves, or are much paler, producing a cryptic effect that helps the butterflies blend into their surroundings.
Ectasia, also called ectasis, is dilation or distention of a tubular structure, either normal or pathophysiologic but usually the latter.
Phlebitis is inflammation of a vein, usually in the legs. It most commonly occurs in superficial veins. Phlebitis often occurs in conjunction with thrombosis and is then called thrombophlebitis or superficial thrombophlebitis. Unlike deep vein thrombosis, the probability that superficial thrombophlebitis will cause a clot to break up and be transported in pieces to the lung is very low.

The ansa cervicalis is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root and an inferior root - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated within the carotid sheath.

Boudinage is a geological term for structures formed by extension, where a rigid tabular body such as hornfels, is stretched and deformed amidst less competent surroundings. The competent bed begins to break up, forming sausage-shaped boudins. Boudinage is common and can occur at any scale, from microscopic to lithospheric, and can be found in all terranes. In lithospheric-scale tectonics, boudinage of strong layers can signify large-scale creep transfer of rock matter. The study of boudinage can also help provide insight into the forces involved in tectonic deformation of rocks and their strength.

Degeneria is a genus of flowering plants endemic to Fiji. It is the only genus in the family Degeneriaceae. The APG IV system of 2016, recognizes this family, and assigns it to the order Magnoliales in the clade magnoliids.

Eupomatia is a genus of three species of plants in the ancient family Eupomatiaceae, and is the sole genus in the family. Eupomatiaceae is recognised by most taxonomists and classified in the plant order Magnoliales. The three described species are shrubs or small trees, native to the rainforests and humid eucalypt forests of eastern Australia and New Guinea. The type species Eupomatia laurina was described in 1814 by Robert Brown.
Kim Kyung-jae was the first human being to die from playing video games too much. He died of deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) after playing the Webzen video game Mu for 86 hours in Gwangju, with pauses only to purchase cigarettes and to use the bathroom. No medical report is available in English. Prolonged immobility as well as vein condition are diatheses that increase the odds of contracting deep vein thrombosis.
The esophageal veins drain blood from the esophagus to the azygos vein, in the thorax, and to the inferior thyroid vein in the neck. It also drains, although with less significance, to the hemiazygos vein, posterior intercostal vein and bronchial veins.

The efferent vessels of the tracheobronchial lymph nodes ascend upon the trachea and unite with efferents of the internal mammary and anterior mediastinal glands to form the right and left bronchomediastinal trunks.
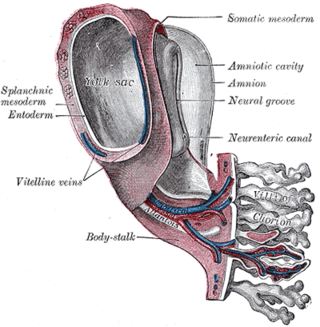
The vitelline arteries are the arterial counterpart to the vitelline veins. Like the veins, they play an important role in the vitelline circulation of blood to and from the yolk sac of a fetus. They are a branch of the dorsal aorta.

Anterior spinal veins are veins that receive blood from the anterior spinal cord.

The anterior intercostal veins are the veins which drain the anterior intercostal space.
Thymic veins are veins which drain the thymus. They are tributaries of the left brachiocephalic vein.

Lamina affixa is a layer of epithelium growing on the surface of the thalamus and forming the floor of the central part of lateral ventricle, on whose medial margin is attached the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle; it covers the superior thalamostriate vein and the superior choroid vein. The torn edge of this plexus is called the tela choroidea.
The vein of bulb of penis is a tributary of the internal pudendal vein.
The deep dorsal vein of clitoris is a vein which drains to the vesical plexus.
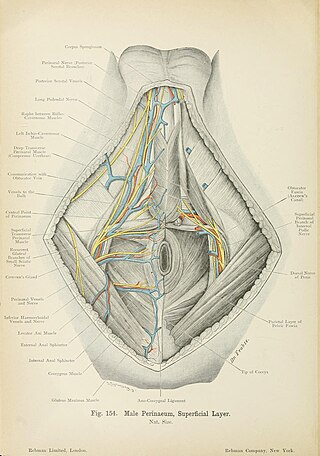
The posterior scrotal veins are veins of the scrotum. They accompany the posterior scrotal arteries. They drain into the vesical venous plexus. They help to drain blood from part of the scrotum.

The posterior labial veins are veins which drain to the vesical venous plexus.

The danger space or alar space, is a region of the neck. The common name originates from the risk that an infection in this space can spread directly to the thorax, and, due to being a space continuous on the left and right, can furthermore allow infection to spread easily to either side.