Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

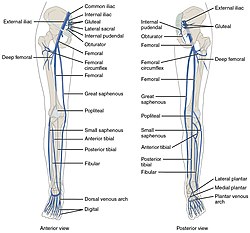
The popliteal vein is a vein of the lower limb. It is formed from the anterior tibial vein and the posterior tibial vein. It travels medial to the popliteal artery, and becomes the femoral vein. It drains blood from the leg. It can be assessed using medical ultrasound. It can be affected by popliteal vein entrapment.
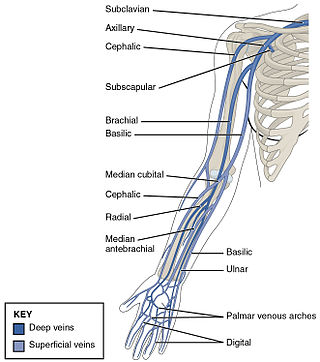
In human anatomy, the brachial veins are venae comitantes of the brachial artery in the arm proper. Because they are deep to muscle, they are considered deep veins. Their course is that of the brachial artery : they begin where radial veins and ulnar veins join. They end at the inferior border of the teres major muscle. At this point, the brachial veins join the basilic vein to form the axillary vein.
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery.

The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.

The ulnar veins are venae comitantes of the ulnar artery. They drain the superficial venous palmar arch. They arise in the hand and terminate by uniting with the radial veins to form the brachial veins. They mostly drain the medial aspect of the forearm. They receive the venae comitantes of the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries near the elbow, as well as a large branch from the median cubital vein. The ulnar veins are larger than the radial veins.
In human anatomy, iliac vein refers to several anatomical structures located in the pelvis:
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

In human anatomy, the superior epigastric veins are two or more venae comitantes which accompany either superior epigastric artery before emptying into the internal thoracic vein. They participate in the drainage of the superior surface of the diaphragm.
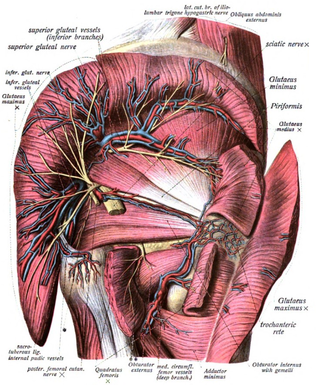
The superior gluteal veins are venæ comitantes of the superior gluteal artery. They receive tributaries from the buttock corresponding with the branches of the artery. They enter the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, superior to the piriformis. They drain into internal iliac vein.

The median sacral artery is a small artery that arises posterior to the abdominal aorta and superior to its bifurcation.
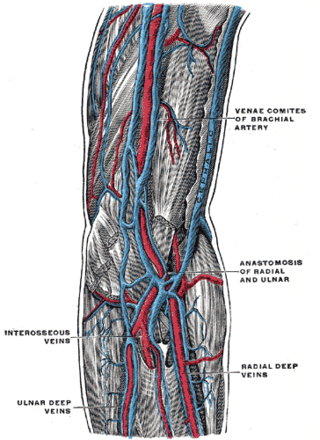
Vena comitans is Latin for accompanying vein and is also known as a satellite vein. It refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes.

The internal pudendal veins are a set of veins in the pelvis. They are the venae comitantes of the internal pudendal artery. Internal pudendal veins are enclosed by pudendal canal, with internal pudendal artery and pudendal nerve.

The lumbar veins are four pairs of veins running along the inside of the posterior abdominal wall, and drain venous blood from parts of the abdominal wall. Each lumbar vein accompanies a single lumbar artery. The lower two pairs of lumbar veins all drain directly into the inferior vena cava, whereas the fate of the upper two pairs is more variable.

The deep circumflex iliac vein is formed by the union of the venae comitantes of the deep iliac circumflex artery, and joins the external iliac vein about 2 cm. above the inguinal ligament. It also receives small tributary branches from the thoracoepigastric vein

The anterior compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles that produce dorsiflexion and participate in inversion and eversion of the foot, as well as vascular and nervous elements, including the anterior tibial artery and veins and the deep fibular nerve.

In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk.
An angiosome is a three-dimensional unit of skin and underlying tissues vascularized by a source artery, termed an arteriosome and drained by a vein termed a venosome. It is a concept that is used by plastic surgeons, and other medical disciplines like CMF, ENT, etc., for the design and harvesting of free flap transplants, and by vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists for the endovascular treatment of critical limb ischemia. It is an alternative model to the traditional "best vessel" model.