
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

The metatarsal bones or metatarsus are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal. The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. A bovine hind leg has two metatarsals.
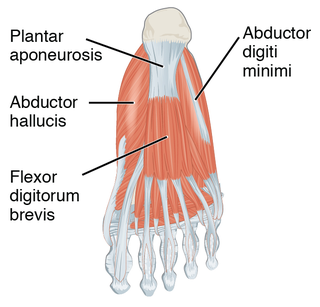
The plantar fascia or plantar aponeurosis is the thick connective tissue aponeurosis which supports the arch on the bottom of the foot. Recent studies suggest that the plantar fascia is actually an aponeurosis rather than true fascia. It runs from the tuberosity of the calcaneus forward to the heads of the metatarsal bones.
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space. It carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei of the foot are four muscles situated between the metatarsal bones.

In human anatomy, plantar interossei muscles are three muscles located between the metatarsal bones in the foot.
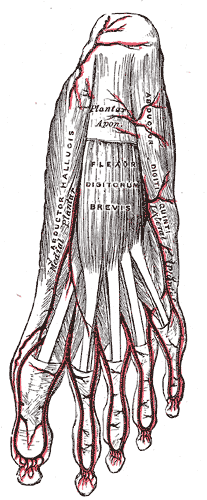
The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.

The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight.

The lateral plantar artery, much larger than the medial, passes obliquely lateralward and forward to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.

The plantar metatarsal arteries are four in number, arising from the convexity of the plantar arch. They run forward between the metatarsal bones and in contact with the Interossei. They are located in the fourth layer of the foot.

The medial plantar artery, much smaller than the lateral plantar artery, passes forward along the medial side of the foot.

The deep plantar artery descends into the sole of the foot, between the two heads of the 1st interosseous dorsalis, and unites with the termination of the lateral plantar artery, to complete the plantar arch.
The plantar digital veins arise from plexuses on the plantar surfaces of the digits, and, after sending intercapitular veins to join the dorsal digital veins, unite to form four metatarsal veins.

The plantar arch is a circulatory anastomosis formed from:
On the dorsum of the foot the dorsal digital veins receive, in the clefts between the toes, the intercapitular veins from the plantar venous arch and join to form short common digital veins which unite across the distal ends of the metatarsal bones in a dorsal venous arch.

The four plantar metatarsal veins run backward in the metatarsal spaces, communicate, by means of perforating veins, with the veins on the dorsum of the foot, and unite to form the plantar venous arch which lies alongside the plantar arterial arch.
The arcuate artery of the foot gives off the second, third, and fourth dorsal metatarsal arteries, which run forward upon the corresponding Interossei dorsales; in the clefts between the toes, each divides into two dorsal digital branches for the adjoining toes.
In the human foot, the plantar or volar plates are fibrocartilaginous structures found in the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints. The anatomy and composition of the plantar plates are similar to the palmar plates in the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal joints in the hand; the proximal origin is thin but the distal insertion is stout. Due to the weight-bearing nature of the human foot, the plantar plates are exposed to extension forces not present in the human hand.










