| Round ligament of the uterus | |
|---|---|
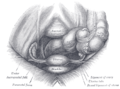
 Cross-section through the pelvis of a newly born female child. (Round ligament labelled at upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Lower gubernaculum [1] |
| Artery | Uterine artery, artery of round ligament of uterus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum teres uteri |
| MeSH | D012404 |
| TA98 | A09.1.03.029 |
| TA2 | 3835 |
| FMA | 20420 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
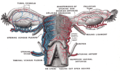
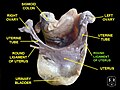
The round ligament of the uterus is a ligament that connects the uterus to the labia majora. It originates at the junction of the uterus and uterine tube. It passes through the inguinal canal to insert at the labium majus.
Contents
- Structure
- Blood supply
- Development
- Function
- Pregnancy
- Additional images
- See also
- References
- External links
The two round ligaments of uterus develop from the gubernaculum; they are the female homologue of the male gubernaculum testis. [2]