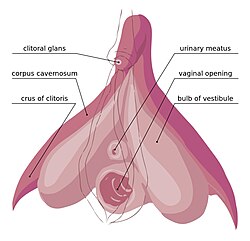
In amniotes, the clitoris is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 nerve endings.

In male human anatomy, the glans penis or penile glans, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. The glans penis is present in the male reproductive organs of humans and most other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is located over the distal ends of the corpora cavernosa and is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by a fold of skin called the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an erection.

Priapism is a condition in which a penis remains erect for hours in the absence of stimulation or after stimulation has ended. There are three types: ischemic (low-flow), nonischemic (high-flow), and recurrent ischemic (intermittent). Most cases are ischemic. Ischemic priapism is generally painful while nonischemic priapism is not. In ischemic priapism, most of the penis is hard; however, the glans penis is not. In nonischemic priapism, the entire penis is only somewhat hard. Very rarely, clitoral priapism occurs in women.

In female humans and other mammals, the clitoral hood is a fold of skin that surrounds and protects the glans of the clitoris; it also covers the external clitoral shaft, develops as part of the labia minora and is homologous with the foreskin in the male reproductive system. The clitoral hood is composed of mucocutaneous tissues; these tissues are between the mucous membrane and the skin, and they may have immunological importance because they may be a point of entry of mucosal vaccines.
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body with numerous vascular spaces, or cavernous tissue, that may become engorged with blood. However, tissue that is devoid of or otherwise lacking erectile tissue may also be described as engorging with blood, often with regard to sexual arousal.

The corpus spongiosum is the mass of spongy tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis. It is also called the corpus cavernosum urethrae in older texts.

The bulbospongiosus muscles are a subgroup of the superficial muscles of the perineum. They have a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, these muscles cover the bulb of the penis, while in females, they cover the vestibular bulbs.
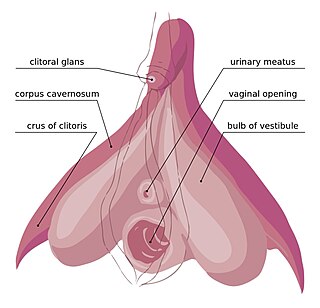
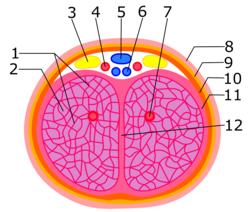
The clitoral crura are two erectile tissue structures, which together form a "V" shape. Crus is a Latin word that means "leg". Each "leg" of the V converges on the clitoral body. At each divergent point is a corpus cavernosum. Together with the vestibular bulbs, they form the clitoral root. The crura are attached to the pubic arch, and are adjacent to the vestibular bulbs. The crura flank the urethra, urethral sponge, and vagina and extend back toward the pubis. Each clitoral crus connects to the rami of the pubis and the ischium.

In female anatomy, the vestibular bulbs, bulbs of the vestibule or clitoral bulbs are two elongated masses of erectile tissue typically described as being situated on either side of the vaginal opening. They are united to each other in front by a narrow median band. Some research indicates that they do not surround the vaginal opening, and are more closely related to the clitoris than to the vestibule. They constitute the root of the clitoris along with the crura.

A corpus cavernosum penis (singular) is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue, which contain most of the blood in the penis during an erection.

The dorsal artery of the penis is a bilaterally paired terminal branch of the internal pudendal artery which passes upon the dorsum of the penis to the base of the glans penis, where it unites with its contralateral partner and supply the glans and foreskin.
The dorsal nerve of the clitoris is a nerve in females that branches off the pudendal nerve to innervate the clitoris. The nerve is important for female sexual pleasure, and it may play a role in clitoral erections.
Venous leak, also called venogenic erectile dysfunction and penile venous insufficiency, is one category of vasculogenic impotence — a cause of erectile dysfunction in males. It affects all ages, being particularly awkward in young men. Much about venous leaks has not reached a consensus among the medical community, and many aspects of the condition, particularly its treatment strategies, are controversial. The prevalence of the condition is still unknown, although some sources claim it to be a common cause of erectile dysfunction.
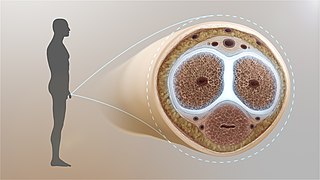
The tunica albuginea is the fibrous envelope that extends the length of the corpus cavernosum penis and corpus spongiosum penis. It is a bi-layered structure that includes an outer longitudinal layer and an inner circular layer.

The two crura of penis constitute the root of penis along with the bulb of penis. The two crura flank the bulb - one to each side of the bulb. Each crus is attached at the angle between the perineal membrane and ischiopubic ramus. The deep artery of the penis enters the anterior portion of the crus. Distally, each crus transitions into either corpus spongiosum of the body of the penis.

The body or shaft of the penis is the free portion of the human penis that is located outside of the pelvic cavity. It is the continuation of the internal root, which is embedded in the pelvis and extends to the glans. It is made up of the two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum on the underside. The corpora cavernosa are intimately bound to one another with a dorsally fenestrated septum, which becomes a complete one before the penile crura. The body of the penis is homologous to the female clitoral body.

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis, which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.

An erection is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal, sexual attraction or libido, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection vary considerably between humans.

Clitoral erection is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm.
Penile ultrasonography is medical ultrasonography of the penis. Ultrasound is an excellent method for the study of the penis, such as indicated in trauma, priapism, erectile dysfunction or suspected Peyronie's disease.