This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2009) |
| Corpus cavernosum penis | |
|---|---|
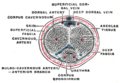
 Transverse section of the penis. | |
 The constituent cavernous cylinders of the penis. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Penis |
| Artery | Cavernous artery [1] |
| Vein | Internal pudendal veins [1] |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | corpus cavernosum penis |
| TA98 | A09.4.01.014 |
| TA2 | 3678 |
| FMA | 19618 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A corpus cavernosum penis (singular) (from Latin, characterised by "cavities/ hollows" [2] of the penis, pl.: corpora cavernosa) is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue, which contain most of the blood in the penis of several animals during an erection. [3] [4] [5] [6]
Contents
It is homologous to the corpus cavernosum clitoridis in the female.