Erectile tissue is tissue in the body with numerous vascular spaces, or cavernous tissue, that may become engorged with blood. However, tissue that is devoid of or otherwise lacking erectile tissue may also be described as engorging with blood, often with regard to sexual arousal.

The corpus spongiosum is the mass of spongy tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis. It is also called the corpus cavernosum urethrae in older texts.

The bulbospongiosus muscles are a subgroup of the superficial muscles of the perineum. They have a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, these muscles cover the bulb of the penis, while in females, they cover the vestibular bulbs.
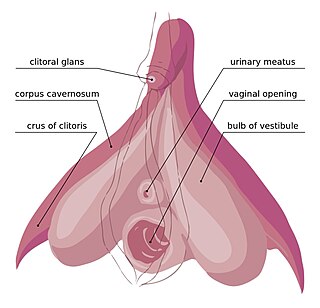
The clitoral crura are two erectile tissue structures, which together form a "V" shape. Crus is a Latin word that means "leg". Each "leg" of the V converges on the clitoral body. At each divergent point is a corpus cavernosum. Together with the vestibular bulbs, they form the clitoral root. The crura are attached to the pubic arch, and are adjacent to the vestibular bulbs. The crura flank the urethra, urethral sponge, and vagina and extend back toward the pubis. Each clitoral crus connects to the rami of the pubis and the ischium.

In female anatomy, the vestibular bulbs, bulbs of the vestibule or clitoral bulbs are two elongated masses of erectile tissue typically described as being situated on either side of the vaginal opening. They are united to each other in front by a narrow median band. Some research indicates that they do not surround the vaginal opening, and are more closely related to the clitoris than to the vestibule. They constitute the root of the clitoris along with the crura.

The ischium forms the lower and back region of the hip bone.

The membranous layer of the superficial fascia of the perineum is the deeper layer of the superficial perineal fascia. It is thin, aponeurotic in structure, and of considerable strength, serving to bind down the muscles of the root of the penis. Colles' fascia emerges from the perineal membrane, which divides the base of the penis from the prostate. Colles' fascia emerges from the inferior side of the perineal membrane and continues along the ventral (inferior) penis without covering the scrotum. It separates the skin and subcutaneous fat from the superficial perineal pouch.

A corpus cavernosum penis (singular) is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue, which contain most of the blood in the penis during an erection.

The corpus cavernosum of clitoris is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue of the clitoris. It is made of a sponge-like tissue that fills with blood during erection. This is homologous to the corpus cavernosum penis. The term corpora cavernosa literally means "cave-like bodies".

The deep artery of the penis is a branch of the internal pudendal artery that supplies the corpus spongiosum. The artery enters the crus of penis at its anterior extremity.

The perineal membrane is an anatomical term for a fibrous membrane in the perineum. The term "inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm", used in older texts, is considered equivalent to the perineal membrane.

The superficial perineal pouch is a compartment of the perineum.

The urogenital triangle is the anterior part of the perineum. In female mammals, it contains the vagina and associated parts of the internal genitalia.

In human male anatomy, the dorsal veins of the penis are blood vessels that drain the shaft, the skin and the glans of the human penis. They are typically located in the midline on the dorsal aspect of the penis and they comprise the superficial dorsal veinof the penis, that lies in the subcutaneous tissue of the shaft, and the deep dorsal veinof the penis, that lies beneath the deep fascia.
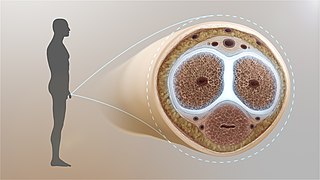
The tunica albuginea is the fibrous envelope that extends the length of the corpora cavernosa penis and corpus spongiosum penis. It is a bi-layered structure that includes an outer longitudinal layer and an inner circular layer.

The bulb of penis is the proximal/posterior end of the corpus spongiosum. Together with the two crura, it constitutes the root of the penis. It is covered by the bulbospongiosus.

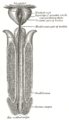
In human anatomy, the penis is an external male sex organ that additionally serves as the urinary duct. The main parts are the root, body, the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the opening, the urinary meatus. It is a passage both for excretion of urine and the ejaculation of semen.

The body or shaft of the penis is the free portion of the human penis that is located outside of the pelvic cavity. It is the continuation of the internal root, which is embedded in the pelvis and extends to the glans. It is made up of the two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum on the underside. The corpora cavernosa are intimately bound to one another with a dorsally fenestrated septum, which becomes a complete one before the penile crura. The body of the penis is homologous to the female clitoral body.

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis, which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.

In human male anatomy, the septum of the penis or penile septum refers to the fibrous junction (septum) between the two corpora cavernosa of the human penis. The tunica albuginea of the penis forms a thick fibrous coat to the spongy tissue of the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum. The two corpora cavernosa are surrounded by a strong fibrous envelope consisting of superficial and deep fibers. The superficial or outer fibers are longitudinal in direction, and form a single tube which encloses both corpora; the deep or inner fibers are arranged circularly around each corpus and meet in the center. By their junction in the median plane, the inner fibers form the intercavernous septum of the penis.