Duct tape, also referred to as duck tape, is cloth- or scrim-backed pressure-sensitive tape, often coated with polyethylene. There are a variety of constructions using different backings and adhesives, and the term 'duct tape' is often used to refer to all sorts of different cloth tapes of differing purposes. Duct tape is often confused with gaffer tape. Another variation is heat-resistant foil duct tape useful for sealing heating and cooling ducts, produced because standard duct tape fails quickly when used on heating ducts. Duct tape is generally silvery gray, but also available in other colors and even printed designs.

The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2 turns(full) and a 3/4(3 quarters) turn around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea.

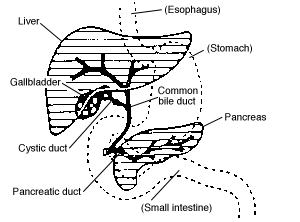
In vertebrates, the gallbladder is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats.
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates.

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the left lymphatic duct, alimentary duct, chyliferous duct, and Van Hoorne's canal. The other duct is the right lymphatic duct. It carries chyle, a liquid containing both lymph and emulsified fats, rather than pure lymph. Thus when it ruptures, the resulting flood of liquid into the pleural cavity is known as chylothorax.

The vas deferens, also called ductus deferens, is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates; these ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. It is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal.
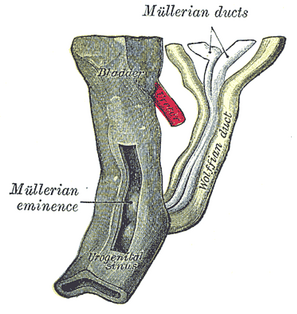
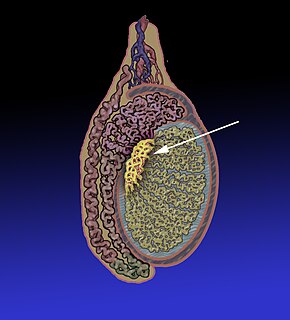
The mesonephric duct is a paired organ found in mammals including humans during embryogenesis. Wolffian structures are male urogenital structures that include the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles that differentiate from this structure.

A ducted fan is a propulsion arrangement whereby a mechanical fan, which is a type of propeller, is mounted within a cylindrical shroud or duct. The duct reduces losses in thrust from the tips of the props, and varying the cross-section of the duct allows the designer to advantageously affect the velocity and pressure of the airflow according to Bernoulli's principle. Ducted fan propulsion is used in aircraft, airships, airboats, hovercraft and fan packs.

The collecting duct system of the kidney consists of a series of tubules and ducts that physically connect nephrons to a minor calyx or directly to the renal pelvis. The collecting duct system participates in electrolyte and fluid balance through reabsorption and excretion, processes regulated by the hormones aldosterone and vasopressin.

The common bile duct, sometimes abbreviated CBD, is a duct in the gastrointestinal tract of organisms that have a gall bladder. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and the cystic duct. It is later joined by the pancreatic duct to form the ampulla of Vater. There, the two ducts are surrounded by the muscular sphincter of Oddi.

Paramesonephric ducts are paired ducts of the embryo that run down the lateral sides of the urogenital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. In the female, they will develop to form the uterine tubes, uterus, cervix, and the upper two third of the vagina. Lower 1/3 of vagina is derived from sinovaginal bulb derived from urogenital sinus; in the male, they are lost. These ducts are made of tissue of mesodermal origin.

The nasolacrimal duct carries tears from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity. The duct begins in the eye socket between the maxillary and lacrimal bones, from where it passes downwards and backwards. The opening of the nasolacrimal duct into the inferior nasal meatus of the nasal cavity is partially covered by a mucosal fold. Excess tears flow through nasolacrimal duct which drains into the inferior nasal meatus.

Common bile duct stone, also known as choledocholithiasis, is the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD). This condition can cause jaundice and liver cell damage. Treatment is by cholecystectomy and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
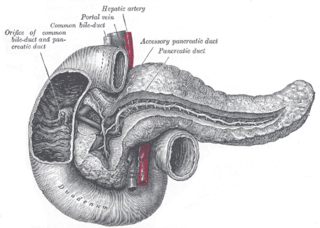
The pancreatic duct, or duct of Wirsung, is a duct joining the pancreas to the common bile duct to supply pancreatic juice provided from the exocrine pancreas, which aids in digestion. The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct just prior to the ampulla of Vater, after which both ducts perforate the medial side of the second portion of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla. There are many anatomical variants reported, but these are quite rare.

Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or malignancy, and metabolic types of cholestasis which are disturbances in bile formation that can occur because of genetic defects or acquired as a side effect of many medications.
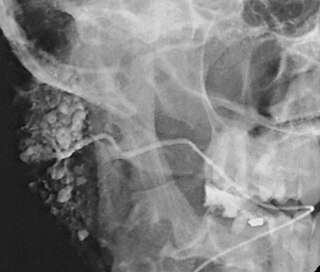
Sialography is the radiographic examination of the salivary glands. It usually involves the injection of a small amount of contrast medium into the salivary duct of a single gland, followed by routine X-ray projections.

Ascending cholangitis, also known as acute cholangitis or simply cholangitis, is inflammation of the bile duct (cholangitis), usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum. It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.

Ducts are conduits or passages used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) to deliver and remove air. The needed airflows include, for example, supply air, return air, and exhaust air. Ducts commonly also deliver ventilation air as part of the supply air. As such, air ducts are one method of ensuring acceptable indoor air quality as well as thermal comfort.

The biliary tract, refers to the liver, gall bladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and conjugated bilirubin. Some components are synthesised by hepatocytes, the rest are extracted from the blood by the liver.
The development of the reproductive system is a part of prenatal development, and concerns the sex organs. It is a part of the stages of sexual differentiation. Because its location, to a large extent, overlaps the urinary system, the development of them can also be described together as the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.