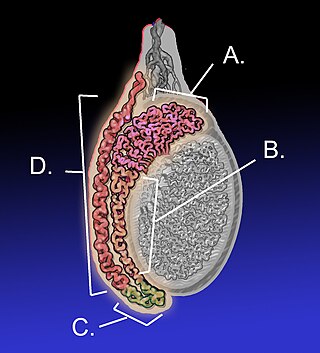
The epididymis is an elongated tubular structure attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, 6 to 7 centimetres in length; uncoiled the tube would be approximately 6 m long. It connects the testicle to the vas deferens in the male reproductive system. The epididymis serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Its primary function is the storage, maturation and transport of sperm cells.

The vas deferens, with the more modern name ductus deferens, is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymides to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal.

The mesonephric duct, also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct, is a paired organ that develops in the early stages of embryonic development in humans and other mammals. It is an important structure that plays a critical role in the formation of male reproductive organs. The duct is named after Caspar Friedrich Wolff, a German physiologist and embryologist who first described it in 1759.

The rete testis is an anastomosing network of delicate tubules located in the hilum of the testicle that carries sperm from the seminiferous tubules to the efferent ducts. It is the homologue of the rete ovarii in females. Its function is to provide a site for fluid reabsorption.
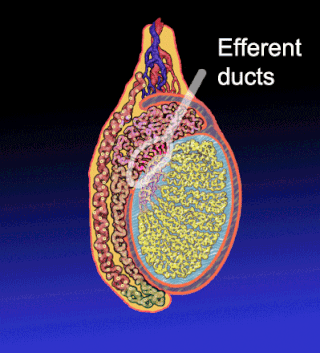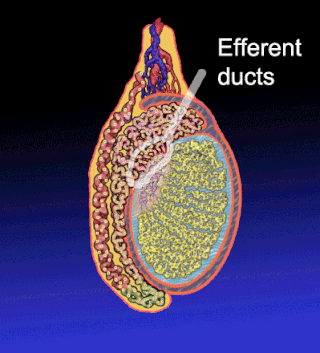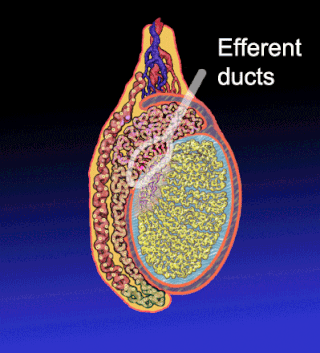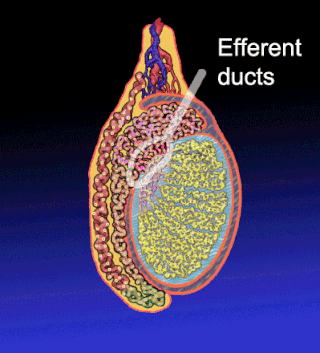
The efferent ducts connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.
The development of the urinary system begins during prenatal development, and relates to the development of the urogenital system – both the organs of the urinary system and the sex organs of the reproductive system. The development continues as a part of sexual differentiation.

The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvis.

The mesonephros is one of three excretory organs that develop in vertebrates. It serves as the main excretory organ of aquatic vertebrates and as a temporary kidney in reptiles, birds, and mammals. The mesonephros is included in the Wolffian body after Caspar Friedrich Wolff who described it in 1759.
The tunica albugine is a dense, blue-white layer of fibrous tissue surrounding the testis. It is the middle of three enveloppes forming the capsule of the testis; it is deep to the visceral layer of tunica vaginalis, and superficial to the tunica vasculosa testis.
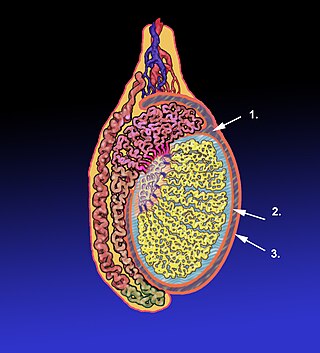
The tunica vaginalis is a pouch of serous membrane within the scrotum that lines the testis and epididymis, and the inner surface of the scrotum. It is the outermost of the three layers that constitute the capsule of the testis, with the tunica albuginea of penis situated beneath it.

The appendix testis is a vestigial remnant of the Müllerian duct, present on the upper pole of the testis and attached to the tunica vaginalis. It is present about 90% of the time and is homologous to the fallopian tubes in females.

The testicular artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles.

The artery to the ductus deferens is an artery in males that provides blood to the ductus deferens.

The mediastinum testis is a thick yet incomplete septum at the posterior part of the testis formed by the tunica albuginea of testis projecting into the testis at its posterior aspect where the testis is not lined by the serous membrane to allow for the attachment of the epididymis. It extends posteriorly between the testis' superior pole and inferior pole. It is wider superiorly than inferiorly. It supports the rete testis and blood and lymphatic vessels of the testis in their passage into and out of the substance of the gland.

Vesicular appendages of the epoöphoron are small pedunculated vesicles of the fimbriae of the uterine tube, or connected to the broad ligament. They were described by Giovanni Battista Morgagni and are remnants of the cranial part of the mesonephric duct. Typically they are asymptomatic.
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system.
The seminal tract is a part of the male reproductive system and consists of Seminiferous tubules, Epididymis (Appendix), Vas deferens (Ampulla) and Ejaculatory duct.

Scrotalultrasound is a medical ultrasound examination of the scrotum. It is used in the evaluation of testicular pain, and can help identify solid masses.
Mammals are the only animals in which the testes descend from their point of origin into a scrotum. Concurrently, mammals are the only class of vertebrates to evolve a prostate gland starting with prostate evolution in monotreme mammals.
The epididymis, which is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system, evolved by retention of the mesonephric duct during regression and replacement of the mesonephros with the metanephric kidney. Similarly, during embryological involution of the paired mesonephric kidneys, each mesonephric duct is retained to become the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle and ejaculatory duct. In reptiles and birds both the testes and excurrent ducts occur in an intra-abdominal location (testicond). Primitive mammals, such as the monotremes (prototheria), also are testicond. Marsupial (metatheria) and placental (eutheria) mammals exhibit differing degrees of testicular descent into an extra-abdominal scrotum. In scrotal mammals the epididymis is attached to the testes in an extra-abdominal position where the cauda epididymis extends beyond the lowest extremity of the testis. Hence, the cauda epididymis is exposed to the coolest of temperatures compared to all other reproductive structures.














