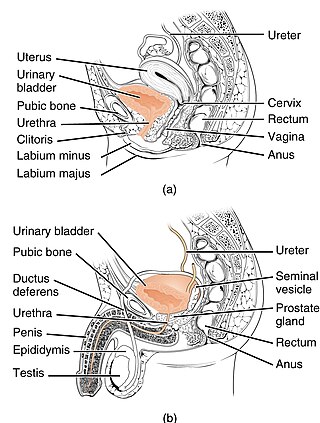
The urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina.
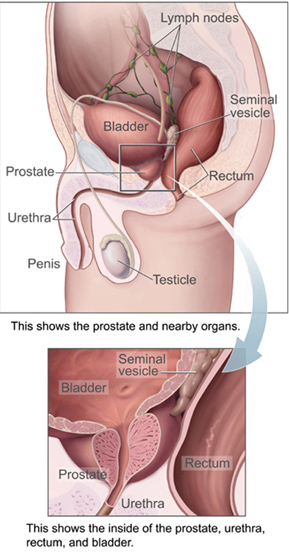
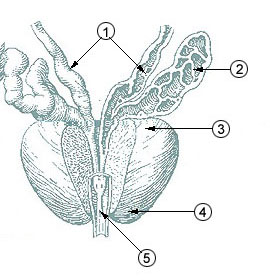
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue, as well as connective tissue.

In female human anatomy, Skene's glands or the Skene glands are glands located around the lower end of the urethra. The glands are surrounded by tissue that swells with blood during sexual arousal, and secrete a fluid from openings near the urethra, particularly during orgasm.

The bulbourethral glands or Cowper's glands are two small exocrine glands in the reproductive system of many male mammals. They are homologous to Bartholin's glands in females. The bulbourethral glands are responsible for producing a pre-ejaculate fluid called Cowper's fluid, which is secreted during sexual arousal, neutralizing the acidity of the urethra in preparation for the passage of sperm cells. The paired glands are found adjacent to the urethra just below the prostate, seen best by screening (medicine) MRI as a tool in preventative healthcare in males. Screening MRI may be performed when there is a positive prostate-specific antigen on basic laboratory tests. Prostate cancer is the second-most common cause of cancer-related mortality in males in the USA.

Retrograde ejaculation occurs when semen which would be ejaculated via the urethra is redirected to the urinary bladder. Normally, the sphincter of the bladder contracts before ejaculation, sealing the bladder which besides inhibiting the release of urine also prevents a reflux of seminal fluids into the male bladder during ejaculation. The semen is forced to exit via the urethra, the path of least resistance. When the bladder sphincter does not function properly, retrograde ejaculation may occur. It can also be induced deliberately by a male as a primitive form of male birth control or as part of certain alternative medicine practices. The retrograde-ejaculated semen, which goes into the bladder, is excreted with the next urination.

The seminal vesicles are a pair of convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.

The vas deferens, with the more modern name ductus deferens or seminiferous tubules or vas efferens, is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymides to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal.

The ejaculatory ducts are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the duct of the seminal vesicle. They pass through the prostate, and open into the urethra above the seminal colliculus. During ejaculation, semen passes through the prostate gland, enters the urethra and exits the body via the urinary meatus.

The paramesonephric ducts are paired ducts of the embryo in the female reproductive system that run down the lateral sides of the genital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. In the female, they will develop to form the fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and the upper one-third of the vagina.
The development of the urinary system begins during prenatal development, and relates to the development of the urogenital system – both the organs of the urinary system and the sex organs of the reproductive system. The development continues as a part of sexual differentiation.

The trigone is a smooth triangular region of the internal urinary bladder formed by the two ureteric orifices and the internal urethral meatus.

The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvis.

The prostatic utricle is a small indentation in the prostatic urethra, at the apex of the urethral crest, on the seminal colliculus (verumontanum), laterally flanked by openings of the ejaculatory ducts. It is also known as the vagina masculina, uterus masculinus or vesicula prostatica.

Posterior urethral valve (PUV) disorder is an obstructive developmental anomaly in the urethra and genitourinary system of male newborns. A posterior urethral valve is an obstructing membrane in the posterior male urethra as a result of abnormal in utero development. It is the most common cause of bladder outlet obstruction in male newborns. The disorder varies in degree, with mild cases presenting late due to milder symptoms. More severe cases can have renal and respiratory failure from lung underdevelopment as result of low amniotic fluid volumes, requiring intensive care and close monitoring. It occurs in about one in 8,000 babies.
The prostatic urethra, the widest and most dilatable part of the urethra canal, is about 3 cm long.

The spongy urethra is the longest part of the male urethra, and is contained in the corpus spongiosum of the penis.

The membranous urethra or intermediate part of male urethra is the shortest, least dilatable, and, with the exception of the urinary meatus, the narrowest part of the urethra.

The urethral crest is an anatomical feature present in the urinary system of both males and females.
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the urogenital or genitourinary system.

The urethral sphincters are two muscles used to control the exit of urine in the urinary bladder through the urethra. The two muscles are either the male or female external urethral sphincter and the internal urethral sphincter. When either of these muscles contracts, the urethra is sealed shut.














