The vas deferens, ductus deferens, or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The vasa deferentia are paired sex organs that transport sperm from the epididymides to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal.

The corpus spongiosum is the mass of spongy tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis. It is also called the corpus cavernosum urethrae in older texts.

The bulbospongiosus muscles are a subgroup of the superficial muscles of the perineum. They have a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, these muscles cover the bulb of the penis, while in females, they cover the vestibular bulbs.

The anterior choroidal artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the brain. It is typically a branch of the internal carotid artery which supplies the choroid plexus of lateral ventricle and third ventricle as well as numerous structures of the brain.

The external anal sphincter is an oval tube of skeletal muscle fibers. Distally, it is adherent to the skin surrounding the margin of the anus. It exhibits a resting state of tonical contraction and also contracts during the bulbospongiosus reflex.
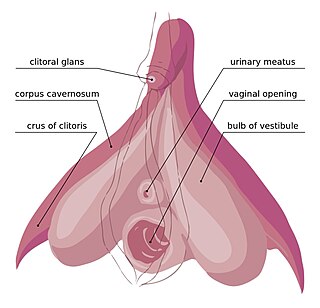
In female anatomy, the vestibular bulbs, bulbs of the vestibule or clitoral bulbs are two elongated masses of erectile tissue typically described as being situated on either side of the vaginal opening. They are united to each other in front by a narrow median band. Some research indicates that they do not surround the vaginal opening, and are more closely related to the clitoris than to the vestibule. They constitute the root of the clitoris along with the crura.

The urethral artery arises from the internal pudendal artery a branch of the internal iliac artery. The internal pudendal artery has numerous branches including the artery of the bulb of the penis immediately before the urethral and the dorsal artery of the penis more distally.

A corpus cavernosum penis (singular) is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue, which contain most of the blood in the penis during an erection.

The dorsal artery of the penis is a bilaterally paired terminal branch of the internal pudendal artery which passes upon the dorsum of the penis to the base of the glans penis, where it unites with its contralateral partner and supply the glans and foreskin.

The artery of bulb of penis is a short artery of large caliber which arises from the internal pudendal artery between the two layers of fascia of the urogenital diaphragm. It passes medialward, pierces the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm and gives off branches which ramify in the bulb of the urethra and in the posterior part of the corpus spongiosum.

The deep artery of the penis is a small collateral branch of the internal pudendal artery that supplies the corpus spongiosum. The artery enters the crus of penis at the crus' anterior extremity.

The perineal membrane is an anatomical term for a fibrous membrane in the perineum. The term "inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm", used in older texts, is considered equivalent to the perineal membrane.

The superficial perineal pouch is a compartment of the perineum.

The urogenital triangle is the anterior part of the perineum. In female mammals, it contains the vulva, while in male mammals, it contains the penis and scrotum.

The spongy urethra is the longest part of the male urethra, and is contained in the corpus spongiosum of the penis.

The membranous urethra or intermediate part of male urethra is the shortest, least dilatable, and, with the exception of the urinary meatus, the narrowest part of the urethra. It extends from the apex of the prostate proximally to the bulb of urethra distally. It measures some 12 mm in length. It traverses the pelvic floor. It is surrounded by the external urethral sphincter, which is in turn envelopped by the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.

The navicular fossa is a short dilated portion of the male urethra within the glans penis just proximal to the external urethral meatus. The roof of the fossa is especially dilated, forming a lacuna; medical instruments being inserted into the male urethra should initially be directed towards the floor of the fossa so as not to get snagged at the fossa. It is one of three dilations of the male urethra.

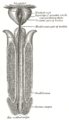
The two crura of penis constitute the root of penis along with the bulb of penis. The two crura flank the bulb – one to each side of the bulb. Each crus is attached at the angle between the perineal membrane and ischiopubic ramus. The deep artery of the penis enters the anterior portion of the crus. Distally, each crus transitions into either corpus spongiosum of the body of the penis.

The posteromedial central arteries or paramedian arteries (also are branches of the posterior cerebral artery, and posterior communicating artery. They entering the substance of the brain through the posterior perforated substance. They supply a large portion of the diencephalon as well as some subcortical telencephalic structures.

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis, which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.