
In male human anatomy, the glans penis or penile glans, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. The glans penis is present in the male reproductive organs of humans and most other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is located over the distal ends of the corpora cavernosa and is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by a fold of skin called the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an erection.

Foreskin restoration is the process of expanding the skin on the penis to reconstruct an organ similar to the foreskin, which has been removed by circumcision or injury. Foreskin restoration is primarily accomplished by stretching the residual skin of the penis, but surgical methods also exist. Restoration creates a facsimile of the foreskin, but specialized tissues removed during circumcision cannot be reclaimed. Actual regeneration of the foreskin is experimental at this time. Some forms of restoration involve only partial regeneration in instances of a high-cut wherein the circumcisee feels that the circumciser removed too much skin and that there is not enough skin for erections to be comfortable.

The perineum in mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx, including the perineal body and surrounding structures. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. This area is also known as the taint or gooch in American slang.

The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side.

The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle that covers the testicles and the spermatic cords in human males. It consists of the lateral and medial parts. Cremaster is an involuntary muscle, responsible for the cremasteric reflex; a protective and physiologic superficial reflex of the testicles. The reflex raises and lowers the testicles in order to keep them protected. Along with the dartos muscle of the scrotum, it regulates testicular temperature, thus aiding the process of spermatogenesis.

The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvis.

Scrotoplasty, also known as oscheoplasty, is a type of surgery to create or repair the scrotum. The history of male genital plastic surgery is rooted in many cultures and dates back to ancient times. However, scientific research for male genital plastic surgery such as scrotoplasty began to develop in the early 1900s. The development of testicular implants began in 1940 made from materials outside of what is used today. Today, testicular implants are created from saline or gel filled silicone rubber. There are a variety of reasons why scrotoplasty is done. Some transgender men and intersex or non-binary people who were assigned female at birth may choose to have this surgery to create a scrotum, as part of their transition. Other reasons for this procedure include addressing issues with the scrotum due to birth defects, aging, or medical conditions such as infection. For newborn males with penoscrotal defects such as webbed penis, a condition in which the penile shaft is attached to the scrotum, scrotoplasty can be performed to restore normal appearance and function. For older male adults, the scrotum may extend with age. Scrotoplasty or scrotal lift can be performed to remove the loose, excess skin. Scrotoplasty can also be performed for males who undergo infection, necrosis, traumatic injury of the scrotum.

The fascia of Scarpa is the deep membranous layer (stratum membranosum) of the superficial fascia of the abdomen. It is a layer of the anterior abdominal wall. It is found deep to the fascia of Camper and superficial to the external oblique muscle.

The fascia of Camper is a thick superficial layer of the anterior abdominal wall.

In human male anatomy, the dorsal veins of the penis are blood vessels that drain the shaft, the skin and the glans of the human penis. They are typically located in the midline on the dorsal aspect of the penis and they comprise the superficial dorsal veinof the penis, that lies in the subcutaneous tissue of the shaft, and the deep dorsal veinof the penis, that lies beneath the deep fascia.

Buck's fascia is a layer of deep fascia covering the three erectile bodies of the penis.

In human anatomy, the penis is an external male sex organ that additionally serves as the urinary duct. The main parts are the root, body, the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus, lies on the tip of the glans. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen.
The development of the gonads is part of the prenatal development of the reproductive system and ultimately forms the testicles in males and the ovaries in females. The immature ova originate from cells from the dorsal endoderm of the yolk sac. Once they have reached the gonadal ridge they are called oogonia. Development proceeds and the oogonia become fully surrounded by a layer of connective tissue cells. In this way, the rudiments of the ovarian follicles are formed.

The subcutaneous tissue of penis is continuous above with the fascia of Scarpa, and below with the dartos tunic of the scrotum and the fascia of Colles.

The subcutaneous tissue of perineum is a layer of subcutaneous tissue surrounding the region of the perineal body.
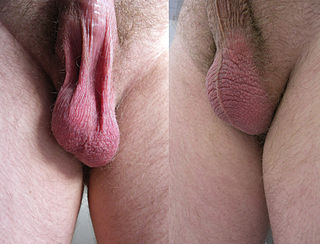
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures.

In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce, is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the glans by an elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum. The outer skin of the foreskin meets with the inner preputial mucosa at the area of the mucocutaneous junction. The foreskin is mobile, fairly stretchable and sustains the glans in a moist environment. Except for humans, a similar structure known as a penile sheath appears in the male sexual organs of all primates and the vast majority of mammals.

Buried penis, also called hidden penis or retractile penis, is a congenital or acquired condition in which the penis is partially or completely hidden below the surface of the skin. A buried penis can lead to urinary difficulties, poor hygiene, infection, and inhibition of normal sexual function.
Male genital examination is a physical examination of the genital in males to detect ailments and to assess sexual development, and is normally a component of an annual physical examination. The examination includes checking the penis, scrotum, and urethral meatus. A comprehensive assessment of the male genitals assesses the pubic hair based on Sexual Maturity Rating and the size of the testicles and penis. The exam can also be conducted to verify a person's age and biological sex. The genitourinary system can also be assessed as part of the male genital examination. During a genital examination, the doctor can detect any of the following: structural abnormalities, urethral opening abnormalities, problems related to not being circumcised, lumps, tumors, redness, excoriation, edema, lesions, swelling, cancer, hair-related issues, and many others. In some instances where a physical examination of the male genitals is not sufficient to diagnose an individual, then an internal genital examination using imaging or ultrasounds will be needed for further evaluation.

The septum of scrotum or scrotal septum is an incomplete vertical wall (septum) that divides the scrotum into two compartments –each containing a single testis. It consists of flexible connective tissue and nonstriated muscle. The site of the median septum is apparent on the surface of the scrotum along a median longitudinal ridge called the scrotal raphe. The perineal raphe further extends forward to the undersurface of the penis and backward to the anal opening. The purpose of the median septum is to compartmentalize each testis in order to prevent friction or trauma.



















