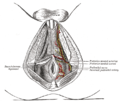
| Ischiocavernosus muscle | |
|---|---|
 Muscles of male perineum (ischiocavernosus visible at upper left) | |
 Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Seen from in front. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Ischial tuberosity |
| Insertion | Crus of penis (male) or crus of clitoris (female) |
| Artery | Perineal artery |
| Nerve | Pudendal nerve |
| Actions | Maintains penile erection (male) or clitoral erection (female) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus ischiocavernosus |
| TA98 | A09.5.02.004 |
| TA2 | 2417 |
| FMA | 19730 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The ischiocavernosus muscle (erectores penisorerector clitoridis in older texts) is a muscle just below the surface of the perineum, present in both men and women. [1]