
The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. There are 60 bones in each leg.

The latissimus dorsi is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part
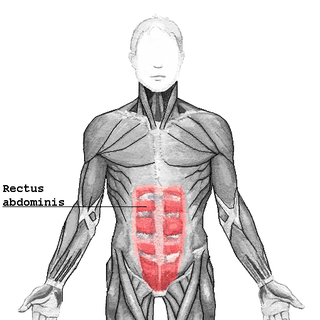
The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline by a band of dense connective tissue called the linea alba, and the connective tissue defining each lateral margin of the rectus abdominus is the linea semilunaris. The muscle extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th–7th ribs superiorly.

In humans and some other mammals, the soleus is a powerful muscle in the back part of the lower leg. It runs from just below the knee to the heel and is involved in standing and walking. It is closely connected to the gastrocnemius muscle, and some anatomists consider this combination to be a single muscle, the triceps surae. Its name is derived from the Latin word "solea", meaning "sandal".

The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral abdominal wall, deep to the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core.

The abdominal internal oblique muscle, also internal oblique muscle or interior oblique, is an abdominal muscle in the abdominal wall that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.

The abdominal external oblique muscle is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.
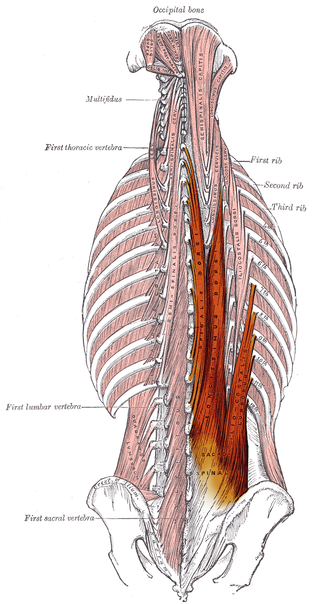
The erector spinae or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.

The thoracolumbar fascia is a complex, multilayer arrangement of fascial and aponeurotic layers forming a separation between the paraspinal muscles on one side, and the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall on the other. It spans the length of the back, extending between the neck superiorly and the sacrum inferiorly. It entails the fasciae and aponeuroses of the latissimus dorsi muscle, serratus posterior inferior muscle, abdominal internal oblique muscle, and transverse abdominal muscle.

The wing(ala)of ilium is the large expanded portion of the ilium, the bone which bounds the greater pelvis laterally. It presents for examination two surfaces—an external and an internal—a crest, and two borders—an anterior and a posterior.

The crest of the ilium is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superiolateral margin of the greater pelvis.
The subcostal arteries, so named because they lie below the last ribs, constitute the lowest pair of branches derived from the thoracic aorta, and are in series with the intercostal arteries.

The arcuate line of rectus sheath is a line of demarcation corresponding to the free inferior margin of the posterior layer of the rectus sheath inferior to which only the anterior layer of the rectus sheath is present and the rectus abdominis muscle is therefore in direct contact with the transversalis fascia. The arcuate line is concave inferior-wards.

The rectus sheath is a tough fibrous compartment formed by the aponeuroses of the transverse abdominal muscle, and the internal and external oblique muscles. It contains the rectus abdominis and pyramidalis muscles, as well as vessels and nerves.

The anterior divisions of the seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, and eleventh thoracic intercostal nerves are continued anteriorly from the intercostal spaces into the abdominal wall; hence they are named thoraco-abdominal nerves.
The lumbar fascia is the lumbar portion of the thoracolumbar fascia. It consists of three fascial layers - posterior, middle, and anterior - that enclose two muscular compartments. The anterior and middle layers occur only in the lumbar region, whereas the posterior layer extends superiorly to the inferior part of the neck, and the inferiorly to the dorsal surface of the sacrum. The quadratus lumborum is contained in the anterior muscular compartment, and the erector spinae in the posterior compartment. Psoas major lies anterior to the anterior layer. Various superficial muscles of the posterior thorax and abdomen arise from the posterior layer - namely the latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior inferior.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The hip bone is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.















