In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
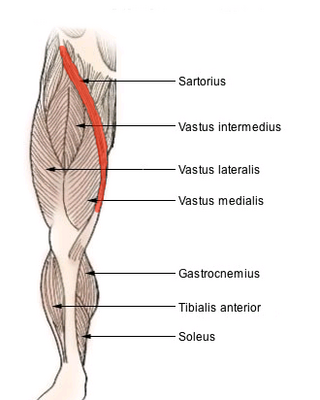
The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that runs down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment.

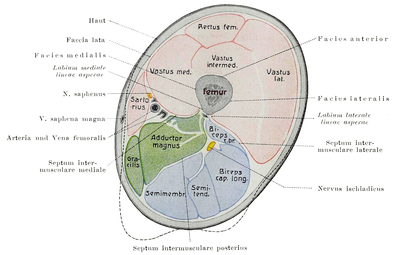
A fascial compartment is a section within the body that contains muscles and nerves and is surrounded by deep fascia. In the human body, the limbs can each be divided into two segments – the upper limb can be divided into the arm and the forearm and the sectional compartments of both of these – the fascial compartments of the arm and the fascial compartments of the forearm contain an anterior and a posterior compartment. Likewise, the lower limbs can be divided into two segments – the leg and the thigh – and these contain the fascial compartments of the leg and the fascial compartments of the thigh.
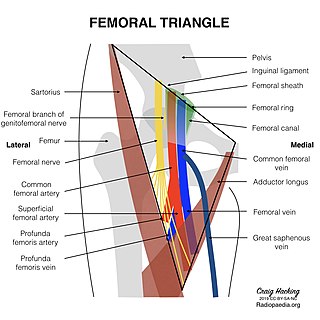
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.

A fascia is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.

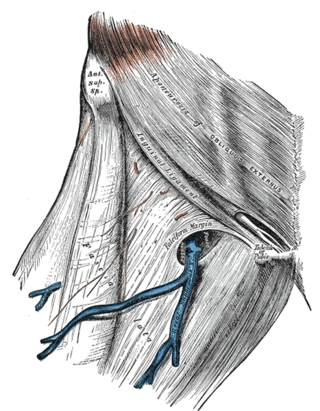
The genitofemoral nerve is a mixed branch of the lumbar plexus derived from anterior rami of L1-L2. It splits a genital branch and a femoral branch. It provides sensory innervation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. It also provides motor innervation to the cremaster muscle.

The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior (front) part of the upper and medial (inner) aspect of the thigh. The pectineus muscle is the most anterior adductor of the hip. The muscle's primary action is hip flexion; it also produces adduction and internal rotation of the hip.

In the human body, the adductor longus is a skeletal muscle located in the thigh. One of the adductor muscles of the hip, its main function is to adduct the thigh and it is innervated by the obturator nerve. It forms the medial wall of the femoral triangle.
The semimembranosus muscle is the most medial of the three hamstring muscles in the thigh. It is so named because it has a flat tendon of origin. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, deep to the semitendinosus muscle. It extends the hip joint and flexes the knee joint.

The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus.
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment.

The masseteric fascia and parotideomasseteric fascia are fascias of the head varyingly described depending upon the source consulted. They may or may not be described as one and the same structure.

The femoral sheath is a funnel-shaped downward extension of abdominal fascia within which the femoral artery and femoral vein pass between the abdomen and the thigh. The femoral sheath is subdivided by two vertical partitions to form three compartments ; the medial compartment is known as the femoral canal and contains lymphatic vessels and a lymph node, whereas the intermediate canal and the lateral canal accommodate the femoral vein and the femoral artery (respectively). Some neurovascular structures perforate the femoral sheath. Topographically, the femoral sheath is contained within the femoral triangle.

The fascial compartments of the leg are the four fascial compartments that separate and contain the muscles of the lower leg. The compartments are divided by septa formed from the fascia. The compartments usually have nerve and blood supplies separate from their neighbours. All of the muscles within a compartment will generally be supplied by the same nerve.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.

The anterior compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles that produce dorsiflexion and participate in inversion and eversion of the foot, as well as vascular and nervous elements, including the anterior tibial artery and veins and the deep fibular nerve.

The posterior compartment of the thigh is one of the fascial compartments that contains the knee flexors and hip extensors known as the hamstring muscles, as well as vascular and nervous elements, particularly the sciatic nerve.

The medial compartment of thigh is one of the fascial compartments of the thigh and contains the hip adductor muscles and the gracilis muscle.

The anterior compartment of thigh contains muscles which extend the knee and flex the hip.

The parapharyngeal space, is a potential space in the head and the neck. It has clinical importance in otolaryngology due to parapharyngeal space tumours and parapharyngeal abscess developing in this area. It is also a key anatomic landmark for localizing disease processes in the surrounding spaces of the neck; the direction of its displacement indirectly reflects the site of origin for masses or infection in adjacent areas, and consequently their appropriate differential diagnosis.