In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the extensor carpi radialis brevis.

The triceps, or triceps brachii, is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of 3 parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint.
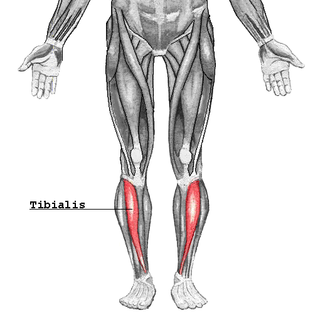
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.

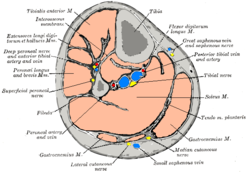
In humans and some other mammals, the soleus is a powerful muscle in the back part of the lower leg. It runs from just below the knee to the heel and is involved in standing and walking. It is closely connected to the gastrocnemius muscle and some anatomists consider it to be a single muscle, the triceps surae. Its name is derived from the Latin word "solea", meaning "sandal".
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.

The extensor digitorum muscle is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. Extensor digitorum is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the radial nerve.

The flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) attaches to the plantar surface of phalanx of the great toe and is responsible for flexing that toe. The FHL is one of the three deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg, the others being the flexor digitorum longus and the tibialis posterior. The tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles. All three muscles are innervated by the tibial nerve which comprises half of the sciatic nerve.
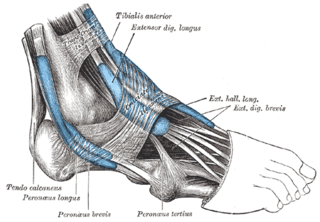
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg.
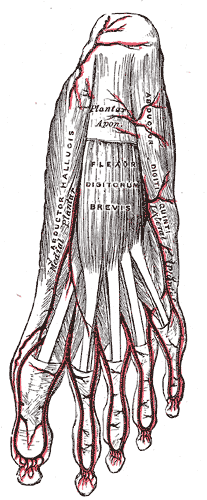
The flexor digitorum brevis is a muscle which lies in the middle of the sole of the foot, immediately above the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, with which it is firmly united.

The palmar aponeurosis invests the muscles of the palm, and consists of central, lateral, and medial portions.
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment.
The antebrachial fascia continuous above with the brachial fascia, is a dense, membranous investment, which forms a general sheath for the muscles in this region; it is attached, behind, to the olecranon and dorsal border of the ulna, and gives off from its deep surface numerous intermuscular septa, which enclose each muscle separately.
The brachial fascia is continuous with that covering the deltoideus and the pectoralis major muscle, by means of which it is attached, above, to the clavicle, acromion, and spine of the scapula; it forms a thin, loose, membranous sheath for the muscles of the arm, and sends septa between them; it is composed of fibers disposed in a circular or spiral direction, and connected together by vertical and oblique fibers.

The fascial compartments of the leg are the four fascial compartments that separate and contain the muscles of the lower leg. The compartments are divided by septa formed from the fascia. The compartments usually have nerve and blood supplies separate from their neighbours. All of the muscles within a compartment will generally be supplied by the same nerve.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.

The posterior compartment of the thigh is one of the fascial compartments that contains the knee flexors and hip extensors known as the hamstring muscles, as well as vascular and nervous elements, particularly the sciatic nerve.

The deep fascia of leg, or crural fascia forms a complete investment to the muscles, and is fused with the periosteum over the subcutaneous surfaces of the bones.

The posterior intermuscular septum of leg, or posterior crural intermuscular septum is a band of fascia which separates the lateral compartment of leg.

The anterior intermuscular septum of leg or anterior crural intermuscular septum is a band of fascia which separates the lateral from the anterior compartment of leg.
Intermuscular septums of the leg may refer to: