
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. There are 60 bones in each leg.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.
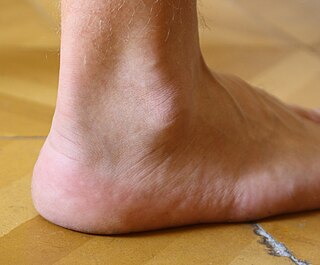
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.

The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) attaches to the plantar surface of phalanx of the great toe and is responsible for flexing that toe. The FHL is one of the three deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg, the others being the flexor digitorum longus and the tibialis posterior. The tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles. All three muscles are innervated by the tibial nerve which comprises half of the sciatic nerve.
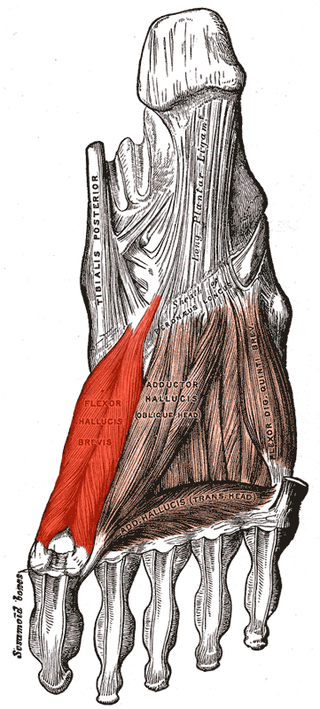
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe.
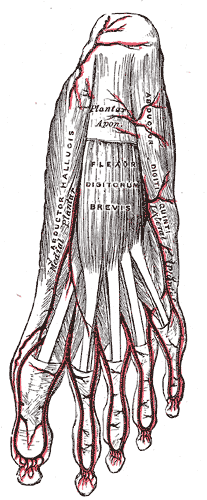
The flexor digitorum brevis or flexor digitorum communis brevis is a muscle which lies in the middle of the sole of the foot, immediately above the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, with which it is firmly united.
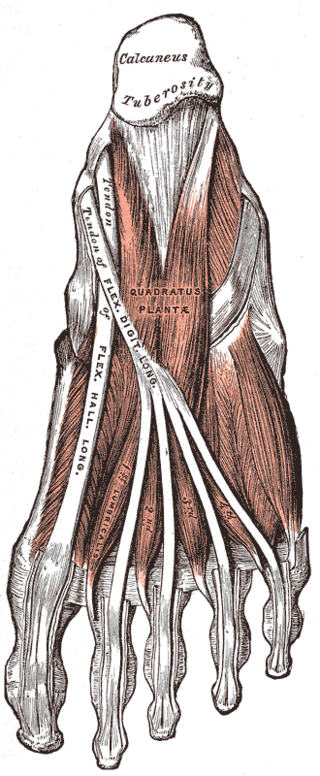
The quadratus plantae is separated from the muscles of the first layer by the lateral plantar vessels and nerve. It acts to aid in flexing the 2nd to 5th toes and is one of the few muscles in the foot with no homolog in the hand.
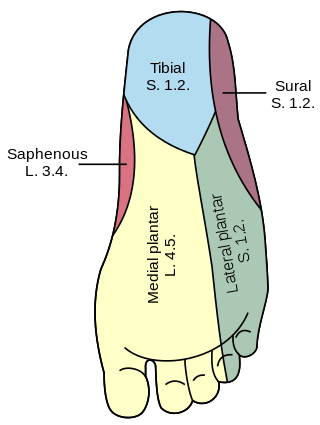
The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.

In humans, the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.
The flexor retinaculum of the foot is a strong fibrous band in the foot.

A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.
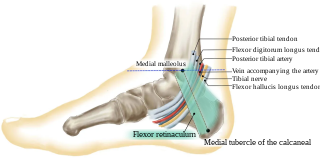
The tarsal tunnel is a passage found along the inner leg underneath the medial malleolus of the ankle.

The tibial malleolar sulcus, also known as the malleolar groove, is the smooth, vertical depression found on the posterior aspect of the medial malleolus. This groove is traversed by the tendons of the tibialis posterior and flexor digitorum longus muscles.



















