The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
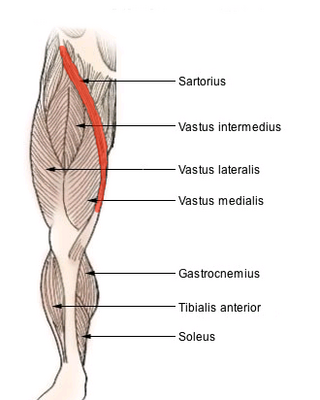
The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that runs down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment.

The deep femoral artery also known as the deep artery of the thigh, or profunda femoris artery, is a large branch of the femoral artery. It travels more deeply ("profoundly") than the rest of the femoral artery. It gives rise to the lateral circumflex femoral artery and medial circumflex femoral artery, and the perforating arteries, terminating within the thigh.

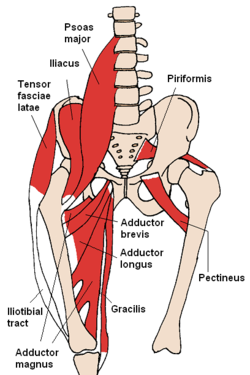
The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior (front) part of the upper and medial (inner) aspect of the thigh. The pectineus muscle is the most anterior adductor of the hip. The muscle's primary action is hip flexion; it also produces adduction and internal rotation of the hip.

In human anatomy, the groin, also known as the inguinal region or iliac region, is the junctional area between the torso and the thigh. The groin is at the front of the body on either side of the pubic tubercle, where the lower part of the abdominal wall meets the thigh. A fold or crease is formed at this junction known as the inguinal groove, or crease. This is also the area of the medial compartment of the thigh that contains attachments of the adductor muscles of the hip or the groin muscles. The groin is the common site for a hernia.

In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxa(pl.: coxae) in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis.

The external obturator muscle or obturator externus muscle is a flat, triangular muscle, which covers the outer surface of the anterior wall of the pelvis.

In the human body, the adductor longus is a skeletal muscle located in the thigh. One of the adductor muscles of the hip, its main function is to adduct the thigh and it is innervated by the obturator nerve. It forms the medial wall of the femoral triangle.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The gracilis muscle is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh. It is thin and flattened, broad above, narrow and tapering below.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.

In human anatomy, the muscles of the hip joint are those muscles that cause movement in the hip. Most modern anatomists define 17 of these muscles, although some additional muscles may sometimes be considered. These are often divided into four groups according to their orientation around the hip joint: the gluteal group; the lateral rotator group; the adductor group; and the iliopsoas group.

The adductor muscles of the hip are a group of muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh mostly used for bringing the thighs together.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; A superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body.

The medial compartment of thigh is one of the fascial compartments of the thigh and contains the hip adductor muscles and the gracilis muscle.
The anterior branch of the obturator nerve is a branch of the obturator nerve found in the pelvis and leg.

In human anatomy, the adductor minimus is a small and flat skeletal muscle in the thigh which constitutes the upper, lateral part of the adductor magnus muscle. It adducts and laterally rotates the femur.