In anatomy and osteology, a foramen is an opening or enclosed gap within the dense connective tissue of extant and extinct amniote animals, typically to allow passage of nerves, arteries, veins or other soft tissue structures from one body compartment to another.

The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior (front) part of the upper and medial (inner) aspect of the thigh. The pectineus muscle is the most anterior adductor of the hip. The muscle's primary action is hip flexion; it also produces adduction and internal rotation of the hip.

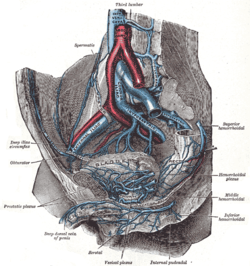
The external iliac veins are large veins that connect the femoral veins to the common iliac veins. Their origin is at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligaments and they terminate when they join the internal iliac veins.

The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.

The adductor brevis is a muscle in the thigh situated immediately deep to the pectineus and adductor longus. It belongs to the adductor muscle group. The main function of the adductor brevis is to pull the thigh medially. The adductor brevis and the rest of the adductor muscle group is also used to stabilize left to right movements of the trunk, when standing on both feet, or to balance when standing on a moving surface. The adductor muscle group is used pressing the thighs together to ride a horse, and kicking with the inside of the foot in soccer or swimming. Last, they contribute to flexion of the thigh when running or against resistance.

In the human body, the adductor longus is a skeletal muscle located in the thigh. One of the adductor muscles of the hip, its main function is to adduct the thigh and it is innervated by the obturator nerve. It forms the medial wall of the femoral triangle.
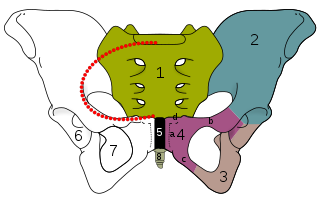
The obturator foramen is the large, bilaterally paired opening of the bony pelvis. It is formed by the pubis and ischium. It is mostly closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening, the obturator canal, through which the obturator nerve and vessels pass.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.

The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch.

The superior hypogastric plexus is a plexus of nerves situated on the vertebral bodies anterior to the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta. It bifurcates to form the left and the right hypogastric nerve. The SHP is the continuation of the abdominal aortic plexus.

The ischioanal fossa is the fat-filled wedge-shaped space located lateral to the anal canal and inferior to the pelvic diaphragm. It is somewhat prismatic in shape, with its base directed to the surface of the perineum and its apex at the line of meeting of the obturator and anal fasciae.

The internal iliac vein begins near the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen, passes upward behind and slightly medial to the internal iliac artery and, at the brim of the pelvis, joins with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein.

The hypogastric nerves are the continuation of the superior hypogastric plexus that descend into the pelvis anterior the sacrum and become the inferior hypogastric plexuses on either side of pelvic organs. The hypogastric nerves serve as a pathway for autonomic fibers to communicate between the lower abdomen and pelvis.

The cardinal ligament is a major ligament of the uterus formed as a thickening of connective tissue of the base of the broad ligament of the uterus. It extends laterally from the cervix and vaginal fornix to attach onto the lateral wall of the pelvis. The female ureter, uterine artery, and inferior hypogastric (nervous) plexus course within the cardinal ligament. The cardinal ligament supports the uterus.

The ovarian fossa is a shallow depression on the lateral wall of the pelvis, where in the ovary lies.

The obturator canal is a passageway formed in the obturator foramen by part of the obturator membrane and the pelvis. It connects the pelvis to the thigh.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy: