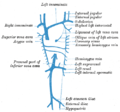
| Internal iliac vein | |
|---|---|
 The veins of the right half of the male pelvis. | |
 The iliac veins. (Int. iliac visible at center.) | |
| Details | |
| Drains from | Pelvic viscera |
| Source | Internal pudendal vein, middle rectal vein, vesical vein, uterine vein, obturator vein, inferior gluteal vein, superior gluteal vein |
| Drains to | Common iliac vein |
| Artery | Internal iliac artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena iliaca interna, vena hypogastrica |
| TA98 | A12.3.10.004 |
| TA2 | 5024 |
| FMA | 18884 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The internal iliac vein (hypogastric vein) begins near the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen, passes upward behind and slightly medial to the internal iliac artery and, at the brim of the pelvis, joins with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein.