Related Research Articles

The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach.

The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine.

The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about 5.5 metres long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter.

The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins.

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.

The bile duct is a part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct. It ends by uniting with the pancreatic duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla. It possesses its own sphincter to enable regulation of bile flow.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach.
The Kocher manoeuvre is a surgical procedure to expose structures in the retroperitoneum behind the duodenum and pancreas. In vascular surgery, it is described as a method to expose the abdominal aorta. It usually has been in contrast to midline laparotomy and right retroperitoneal space dissection. These two procedures have been used for diverse cases, but have approximately equivalent outcomes.
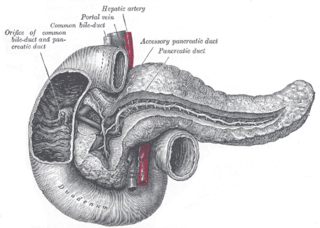
The pancreatic duct or duct of Wirsung is a duct joining the pancreas to the common bile duct. This supplies it with pancreatic juice from the exocrine pancreas, which aids in digestion.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

The pancreatic branches or pancreatic arteries are numerous small vessels derived from the splenic artery as it runs behind the upper border of the pancreas, supplying its body and tail.
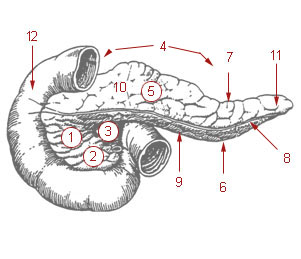
The uncinate process is a small part of the pancreas. The uncinate process is the formed prolongation of the angle of junction of the lower and left lateral borders in the head of the pancreas. The word "uncinate" comes from the Latin "uncinatus", meaning "hooked".

The dorsal pancreatic artery is a branch of the splenic artery. It anastomoses with the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery and continues as the inferior pancreatic artery on its lower border.

Centroacinar cells are spindle-shaped cells in the exocrine pancreas."They are small with microvilli on the apical surface". They work with organs such as the kidney, lungs, stomach, brain, intestine.

The major duodenal papilla is a rounded projection in the duodenum into which the common bile duct and pancreatic duct drain. The major duodenal papilla is, in most people, the primary mechanism for the secretion of bile and other enzymes that facilitate digestion.

The left gastric vein is a vein that derives from tributaries draining the lesser curvature of the stomach.

In the circulatory system of vertebrates, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them are considered part of the portal venous system.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The liver is a major metabolic organ only found in vertebrate animals, which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 681 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 681 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)