The bladder is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.
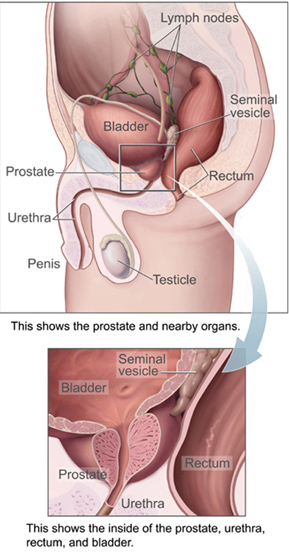
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue, as well as connective tissue.

The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In a human adult, the ureters are usually 20–30 cm (8–12 in) long and around 3–4 mm (0.12–0.16 in) in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer that assists with peristalsis in its lowest third.

A rete mirabile is a complex of arteries and veins lying very close to each other, found in some vertebrates, mainly warm-blooded ones. The rete mirabile utilizes countercurrent blood flow within the net to act as a countercurrent exchanger. It exchanges heat, ions, or gases between vessel walls so that the two bloodstreams within the rete maintain a gradient with respect to temperature, or concentration of gases or solutes. This term was coined by Galen.

A bladder stone is a stone found in the urinary bladder.

The seminal vesicles are a pair of convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.

The trigone is a smooth triangular region of the internal urinary bladder formed by the two ureteric orifices and the internal urethral meatus.

Schistosoma haematobium is a species of digenetic trematode, belonging to a group (genus) of blood flukes (Schistosoma). It is found in Africa and the Middle East. It is the major agent of schistosomiasis, the most prevalent parasitic infection in humans. It is the only blood fluke that infects the urinary tract, causing urinary schistosomiasis, and is the leading cause of bladder cancer. The diseases are caused by the eggs.

A calculus, often called a stone, is a concretion of material, usually mineral salts, that forms in an organ or duct of the body. Formation of calculi is known as lithiasis. Stones can cause a number of medical conditions.
A varix is an abnormally dilated vessel with a tortuous course. Varices usually occur in the venous system, but may also occur in arterial or lymphatic vessels.
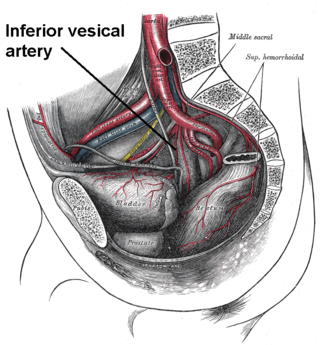
The inferior vesical artery is an artery of the pelvis which arises from the internal iliac artery and supplies parts of the urinary bladder as well as other structures of the urinary system and structures of the male reproductive system.

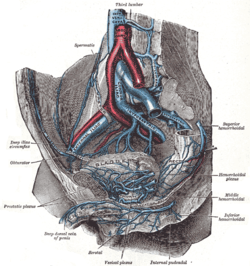
The rectal venous plexus is the venous plexus surrounding the rectum. It consists of an internal and an external rectal plexus. It is drained by the superior, middle, and inferior rectal veins. It forms a portosystemic (portocaval) anastomosis. This allows rectally administered medications to bypassing first pass metabolism.

The prostatic veins form a well-marked prostatic plexus which lies partly in the fascial sheath of the prostate and partly between the sheath and the prostatic capsule. It collects blood from the prostate, and the corpora cavernosa of penis. It communicates with the pudendal and vesical plexuses.

The vaginal venous plexus is a group of veins draining blood from the vagina. It lies around the sides of the vagina. Its blood eventually drains into the internal iliac veins.

The vesical venous plexus is a venous plexus situated at the fundus of the urinary bladder. It collects venous blood from the urinary bladder in both sexes, from the accessory sex glands in males, and from the corpora cavernosa of clitoris in females. It drains into the internal iliac veins via several vesical veins.
The Batson venous plexus is a network of valveless veins in the human body that connect the deep pelvic veins and thoracic veins to the internal vertebral venous plexuses. Because of their location and lack of valves, they are believed to provide a route for the spread of cancer metastases. These metastases commonly arise from cancer of the pelvic organs such as the rectum and prostate and may spread to the vertebral column or brain. The plexus is named after anatomist Oscar Vivian Batson, who first described it in 1940. Batson's plexus is part of the Cerebrospinal venous system.
The pudendal venous plexus lies behind the arcuate pubic ligament and the lower part of the pubic symphysis, and in front of the bladder and prostate. Its chief tributary is the deep dorsal vein of the penis, but it also receives branches from the front of the bladder and prostate. It communicates with the vesical venous plexus and with the internal pudendal vein and drains into the vesical and hypogastric veins.
Vesical refers to the urinary bladder and its relevant and nearby structures and functions, including:
The posterior scrotal veins are veins of the scrotum in men. They accompany the posterior scrotal arteries. They drain into the vesical venous plexus. They help to drain blood from part of the scrotum.
Urinary bladder disease includes urinary bladder inflammation such as cystitis, bladder rupture and bladder obstruction (tamponade). Cystitis is common, sometimes referred to as urinary tract infection (UTI) caused by bacteria, bladder rupture occurs when the bladder is overfilled and not emptied while bladder tamponade is a result of blood clot formation near the bladder outlet.