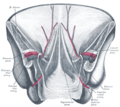
| Inferior epigastric vein | |
|---|---|
 Right inferior epigastric vein - view from inside of abdomen. | |
 The iliac veins. | |
| Details | |
| Drains from | Superior epigastric vein |
| Drains to | External iliac vein |
| Artery | Inferior epigastric artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena epigastrica inferior |
| TA98 | A12.3.10.025 |
| TA2 | 5051 |
| FMA | 21162 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, inferior epigastric vein are 1-2 veins accompanying the inferior epigastric artery. They drain into the external iliac vein just proximal to the inguinal ligament. [1]