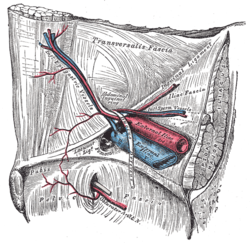
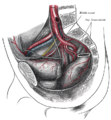
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh.
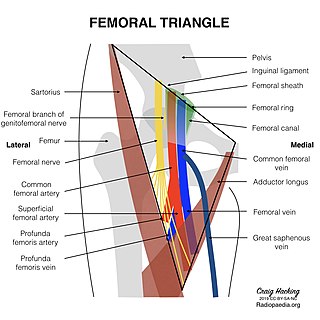
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.

The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body, which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males.

The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

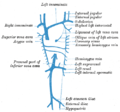
In the human body, the femoral vein is the vein that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It is a deep vein that begins at the adductor hiatus as the continuation of the popliteal vein. The great saphenous vein, and the deep femoral vein drain into the femoral vein in the femoral triangle when it becomes known as the common femoral vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament where it becomes the external iliac vein. Its major tributaries are the deep femoral vein, and the great saphenous vein. The femoral vein contains valves.

In human anatomy, the common iliac veins are formed by the external iliac veins and internal iliac veins. The left and right common iliac veins come together in the abdomen at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra, forming the inferior vena cava. They drain blood from the pelvis and lower limbs.

The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.

The anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, and the sartorius muscle. The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior anterior iliac spine, and also about 5 cm away at the iliac tubercle.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.

The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus.

The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a cutaneous nerve of the thigh. It originates from the dorsal divisions of the second and third lumbar nerves from the lumbar plexus. It passes under the inguinal ligament to reach the thigh. It supplies sensation to the skin on the lateral part of the thigh by an anterior branch and a posterior branch.

The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch.
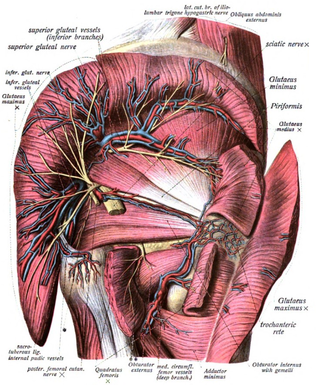
The inferior gluteal veins are venae comitantes of the inferior gluteal artery. They commence in the superior/proximal posterior thigh. They enter the pelvis through the lower part of the greater sciatic foramen. They converge to form a single vessel before emptying into the distal portion of the internal iliac vein.

The lateral umbilical fold is an elevation of the peritoneum lining the inner/posterior surface of the lower anterior abdominal wall formed by the underlying inferior epigastric artery and inferior epigastric vein which the peritoneum covers. Superiorly, the lateral umbilical fold ends where the vessels reach and enter the rectus sheath at the arcuate line of rectus sheath; in spite of the name, the lateral umbilical folds do not extend as far superiorly as the umbilicus. Inferiorly, it extends to just medial to the deep inguinal ring.

The iliac fascia is the fascia overlying the iliacus muscle.

The internal iliac vein begins near the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen, passes upward behind and slightly medial to the internal iliac artery and, at the brim of the pelvis, joins with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein.

The deep circumflex iliac artery is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy: