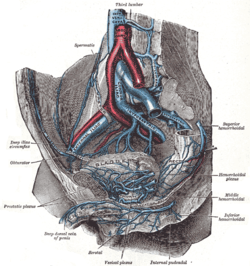
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra.

The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side.

The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.

In human anatomy, the common iliac veins are formed by the external iliac veins and internal iliac veins. The left and right common iliac veins come together in the abdomen at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra, forming the inferior vena cava. They drain blood from the pelvis and lower limbs.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum.

The conus medullaris or conus terminalis is the tapered, lower end of the spinal cord. It occurs near lumbar vertebral levels 1 (L1) and 2 (L2), occasionally lower. The upper end of the conus medullaris is usually not well defined, however, its corresponding spinal cord segments are usually S1–S5.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a cutaneous nerve of the thigh. It originates from the dorsal divisions of the second and third lumbar nerves from the lumbar plexus. It passes under the inguinal ligament to reach the thigh. It supplies sensation to the skin on the lateral part of the thigh by an anterior branch and a posterior branch.

The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.

The median sacral artery is a small artery that arises posterior to the abdominal aorta and superior to its bifurcation.

The lumbar arteries are arteries located in the lower back or lumbar region. The lumbar arteries are in parallel with the intercostals.

The superior hypogastric plexus is a plexus of nerves situated on the vertebral bodies anterior to the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta. It bifurcates to form the left and the right hypogastric nerve. The SHP is the continuation of the abdominal aortic plexus.

The iliolumbar ligament is a strong ligament which attaches medially to the transverse process of the 5th lumbar vertebra, and laterally to back of the inner lip of the iliac crest.

The deep circumflex iliac artery is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone.

The lumbar veins are four pairs of veins running along the inside of the posterior abdominal wall, and drain venous blood from parts of the abdominal wall. Each lumbar vein accompanies a single lumbar artery. The lower two pairs of lumbar veins all drain directly into the inferior vena cava, whereas the fate of the upper two pairs is more variable.

The ascending lumbar vein is a vein that runs up through the lumbar region on the side of the vertebral column.
The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is derived from the lumbar plexus (L3-L4). It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function. It commences in the proximal (upper) thigh and travels along the adductor canal. Upon exiting the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve terminates by splitting into two terminal branches: the sartorial nerve, and the infrapatellar nerve. The saphenous nerve is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin of the anteromedial leg.
The lumbar fascia is the lumbar portion of the thoracolumbar fascia. It consists of three fascial layers - posterior, middle, and anterior - that enclose two muscular compartments. The anterior and middle layers occur only in the lumbar region, whereas the posterior layer extends superiorly to the inferior part of the neck, and the inferiorly to the dorsal surface of the sacrum. The quadratus lumborum is contained in the anterior muscular compartment, and the erector spinae in the posterior compartment. Psoas major lies anterior to the anterior layer. Various superficial muscles of the posterior thorax and abdomen arise from the posterior layer - namely the latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior inferior.

The lumbosacral ligament or lateral lumbosacral ligament is a ligament that helps to stabilise the lumbosacral joint. The ligament's medial attachment is at transverse process of lumbar vertebra L5; its lateral attachment is at the ala of sacrum.