The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins.

Budd–Chiari syndrome is a very rare condition, affecting one in a million adults. The condition is caused by occlusion of the hepatic veins that drain the liver. The symptoms are non-specific and vary widely, but it may present with the classical triad of abdominal pain, ascites, and liver enlargement. It is usually seen in younger adults, with the median age at diagnosis between the ages of 35 and 40, and it has a similar incidence in males and females. The syndrome can be fulminant, acute, chronic, or asymptomatic. Subacute presentation is the most common form.

In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. There are usually three large upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver, as well as a number (6-20) of lower hepatic veins. All hepatic veins are valveless.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament.

In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach before anastomosing with the right gastric artery. It also issues esophageal branches that supply lower esophagus and ascend through the esophageal hiatus to form anastomoses with the esophageal branches of thoracic part of aorta.

Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is an artificial channel within the liver that establishes communication between the inflow portal vein and the outflow hepatic vein. It is used to treat portal hypertension which frequently leads to intestinal bleeding, life-threatening esophageal bleeding and the buildup of fluid within the abdomen (ascites).

Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a vascular disease of the liver that occurs when a blood clot occurs in the hepatic portal vein, which can lead to increased pressure in the portal vein system and reduced blood supply to the liver. The mortality rate is approximately 1 in 10.

The hepatic artery proper is the artery that supplies the liver and gallbladder. It raises from the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac artery.

In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system or portal venous system is the system of veins comprising the portal vein and its tributaries. The other portal venous system in the body is the hypophyseal portal system.

The vitelline veins are veins that drain blood from the yolk sac and the gut tube during gestation.

The porta hepatis or transverse fissure of the liver is a short but deep fissure, about 5 cm long, extending transversely beneath the left portion of the right lobe of the liver, nearer its posterior surface than its anterior border.

Hepatocellular adenoma is a rare, benign liver tumor. It most commonly occurs in people with elevated systemic levels of estrogen, classically in women taking estrogen-containing oral contraceptive medication.

Congestive hepatopathy, is liver dysfunction due to venous congestion, usually due to congestive heart failure. The gross pathological appearance of a liver affected by chronic passive congestion is "speckled" like a grated nutmeg kernel; the dark spots represent the dilated and congested hepatic venules and small hepatic veins. The paler areas are unaffected surrounding liver tissue. When severe and longstanding, hepatic congestion can lead to fibrosis; if congestion is due to right heart failure, it is called cardiac cirrhosis.
The stellate veins are minute veins situated just beneath the fibrous capsule of the kidney. The stellate veins drain the superficial-most portion of the renal cortex. Groups of 5 or 6 stellate veins are arranged in a star-like pattern, converging centrally to drain into an interlobular vein as it penetrates into the renal cortex.

A liver sinusoid is a type of capillary known as a sinusoidal capillary, discontinuous capillary or sinusoid, that is similar to a fenestrated capillary, having discontinuous endothelium that serves as a location for mixing of the oxygen-rich blood from the hepatic artery and the nutrient-rich blood from the portal vein.

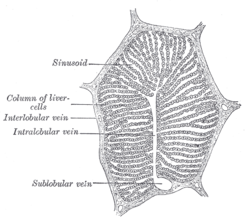
In histology, the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver tissue, consisting of a portal triad, hepatocytes arranged in linear cords between a capillary network, and a central vein.

In human anatomy, the omental foramen is the passage of communication, or foramen, between the greater sac, and the lesser sac.

The liver is a major metabolic organ only found in vertebrate animals, which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells.

Centrilobular necrosis (CN) is a nonspecific histopathological observation brought on by hepatotoxins like acetaminophen (paracetamol), thioacetamide, tetrachloride, cardiac hepatopathy due to acute right sided cardiac failure, and congestive hepatic injury in veno‐occlusive disease, or hypoxic injury due to ischemia. Centrilobular necrosis can also be found in those with autoimmune hepatitis. Centrilobular necrosis is characterized by necrotic hepatocytes completely encircling the central vein.

In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface – the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside – the visceral surface – the other two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are also visible. The two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are known as superficial or accessory lobes, and both are located on the underside of the right lobe.