The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms are often used interchangeably but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal.

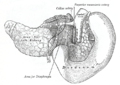
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins.
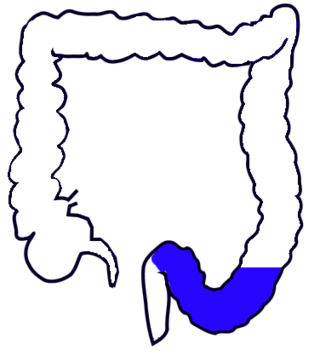
The sigmoid colon is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about 35–40 centimetres (14–16 in) in length. The loop is typically shaped like a Greek letter sigma (ς) or Latin letter S. This part of the colon normally lies within the pelvis, but due to its freedom of movement it is liable to be displaced into the abdominal cavity.

The renal veins in the renal circulation, are large-calibre veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney. Each renal vein is formed by the convergence of the interlobar veins of one kidney.

The celiacartery, also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta.
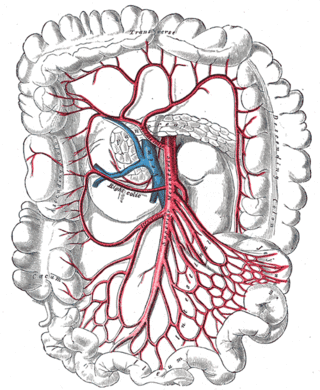
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

In human anatomy, the splenic vein is a blood vessel that drains blood from the spleen, the stomach fundus and part of the pancreas. It is part of the hepatic portal system.

In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system or portal venous system is the system of veins comprising the portal vein and its tributaries. The other portal venous systems in the body are the renal portal system, and the hypophyseal portal system.

The sigmoid arteries are 2–5 branches of the inferior mesenteric artery that are distributed to the distal descending colon and the sigmoid colon.

The middle colic artery is an artery of the abdomen; a branch of the superior mesenteric artery distributed to parts of the ascending and transverse colon. It usually divides into two terminal branches - a left one and a right one - which go on to form anastomoses with the left colic artery, and right colic artery (respectively), thus participating in the formation of the marginal artery of the colon.

The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively).

The ileocolic artery is the lowest branch arising from the concavity of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the cecum, ileum, and appendix.

In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure. Note that "right" refers to the patient's anatomical right, which may be depicted on the left of a diagram.

The superior rectal artery is an artery that descends into the pelvis to supply blood to the rectum.

The pancreatic branches or pancreatic arteries are numerous small vessels derived from the splenic artery as it runs behind the upper border of the pancreas, supplying its body and tail.

In the circulatory system of vertebrates, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them are considered part of the portal venous system.

Peritoneal recesses are the spaces formed by peritoneum draping over viscera.
The superior mesenteric vessels are composed of the superior mesenteric artery and the superior mesenteric vein.