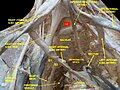
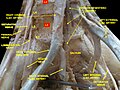
| External iliac artery | |
|---|---|
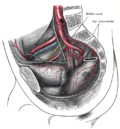
 Front of abdomen, showing common iliac artery, the source of the external iliac artery | |
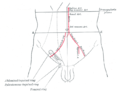
 Volume rendered CT scan of abdominal and pelvic blood vessels. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Common iliac arteries |
| Branches | Femoral arteries, inferior epigastric arteries |
| Vein | External iliac veins |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria iliaca externa |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.002 |
| TA2 | 4357 |
| FMA | 18805 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
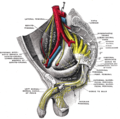
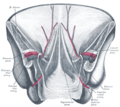
The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.