
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh.
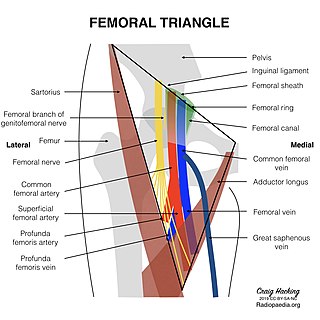
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.

The deep femoral artery also known as the deep artery of the thigh, or profunda femoris artery, is a large branch of the femoral artery. It travels more deeply ("profoundly") than the rest of the femoral artery. It gives rise to the lateral circumflex femoral artery and medial circumflex femoral artery, and the perforating arteries, terminating within the thigh.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus.

The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.

The superior gluteal artery is the terminal branch of the posterior division of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen before splitting into a superficial branch and a deep branch.

The lateral superior genicular artery is a branch of the popliteal artery that supplies a portion of the knee joint.

The lateral circumflex femoral artery is an artery in the upper thigh. It is usually a branch of the profunda femoris artery, and produces three branches. It is mostly distributed to the muscles of the lateral thigh, supplying arterial blood to muscles of the knee extensor group.

The medial circumflex femoral artery is an artery in the upper thigh that arises from the profunda femoris artery. It supplies arterial blood to several muscles in the region, as well as the femoral head and neck.
The cruciate anastomosis is a circulatory anastomosis in the upper thigh formed by the inferior gluteal artery, the lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries, the first perforating artery of the deep femoral artery, and the anastomotic branch of the posterior branch of the obturator artery.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The deep circumflex iliac artery is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone.
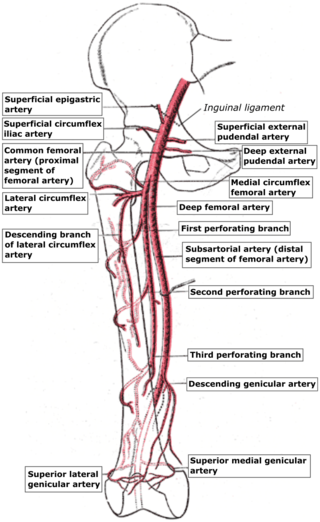
The perforating arteries are branches of the deep artery of the thigh, usually three in number, so named because they perforate the tendon of the adductor magnus to reach the back of the thigh. They pass backward near the linea aspera of the femur underneath the small tendinous arches of the adductor magnus muscle.

The superficial external pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It arises from the medial side of the femoral artery, close to the superficial epigastric artery and superficial iliac circumflex artery.
The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is derived from the lumbar plexus (L3-L4). It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function. It commences in the proximal (upper) thigh and travels along the adductor canal. Upon exiting the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve terminates by splitting into two terminal branches: the sartorial nerve, and the infrapatellar nerve. The saphenous nerve is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin of the anteromedial leg.

The superficial branch of medial circumflex femoral artery appears between the quadratus femoris and upper border of the adductor magnus, and anastomoses with the inferior gluteal artery, lateral femoral circumflex artery, and first of the perforating arteries of the deep femoral artery.

The acetabular branch is an artery in the hip that arises from the medial circumflex femoral artery opposite the acetabular notch and enters the hip-joint beneath the transverse ligament in company with an articular branch from the obturator artery. It supplies the fat in the bottom of the acetabulum, and is continued along the ligament to the head of the femur.
The trochanteric anastomosis is an anatomical structure that provides circulation around the head of the femur. It includes the superior gluteal artery and the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries.

The genicular arteries are six arteries in the human leg, five of which are branches of the popliteal artery, that anastomose in the knee region in the patellar network or genicular anastomosis. They supply blood to the patella, together with contributions from the descending genicular artery, anterior tibial recurrent artery, and descending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery.












