In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

The anterior tibial vein is a vein in the lower leg.
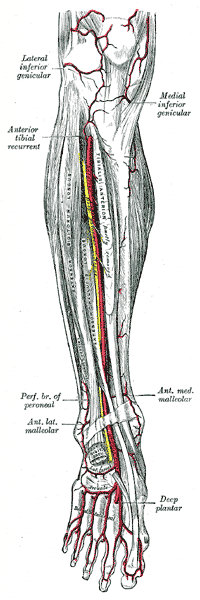
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.

The lateral inferior genicular is an artery of the leg.

The medial inferior genicular is an artery of the leg.
The anterior medial malleolar artery is an artery in the ankle. It arises about 5 cm. above the ankle-joint from the anterior tibial artery.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:
The anterior lateral malleolar artery is an artery in the ankle.
The posterior tibial recurrent artery, an inconstant branch, is given off from the anterior tibial before that vessel passes through the gap between superior tibio-fibular joint and upper border of interosseous membrane.

The descending genicular artery arises from the femoral artery just before its passage through the adductor hiatus.
The sural arteries are two large branches, lateral and medial, which are distributed to the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles. Sural means related to the calf. The term applies to any of four or five arteries arising from the popliteal artery, with distribution to the muscles and integument of the calf, and with anastomoses to the posterior tibial, medial and lateral inferior genicular arteries.

The popliteal lymph nodes, small in size and some six or seven in number, are embedded in the fat contained in the popliteal fossa, sometimes referred to as the 'knee pit'. One lies immediately beneath the popliteal fascia, near the terminal part of the small saphenous vein, and drains the region from which this vein derives its tributaries, such as superficial regions of the posterolateral aspect of the leg and the plantar aspect of the foot.

In human anatomy, the adductor hiatus also known as hiatus magnus is a hiatus (gap) between the adductor magnus muscle and the femur that allows the passage of the femoral vessels from the anterior thigh to the posterior thigh and then the popliteal fossa. It is the termination of the adductor canal and lies about 8–13.5 cm (3.1–5.3 in) superior to the adductor tubercle.

The anterior compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles that produce dorsiflexion and participate in inversion and eversion of the foot, as well as vascular and nervous elements, including the anterior tibial artery and veins and the deep fibular nerve.

The patellar network is an intricate network of blood vessels around and above the patella, and on the contiguous ends of the femur and tibia, forming a superficial and a deep plexus.

In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk.

The genicular arteries are six arteries in the human leg, five of which are branches of the popliteal artery, that anastomose in the knee region in the patellar network or genicular anastomosis. They supply blood to the patella, together with contributions from the descending genicular artery, anterior tibial recurrent artery, and descending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery.