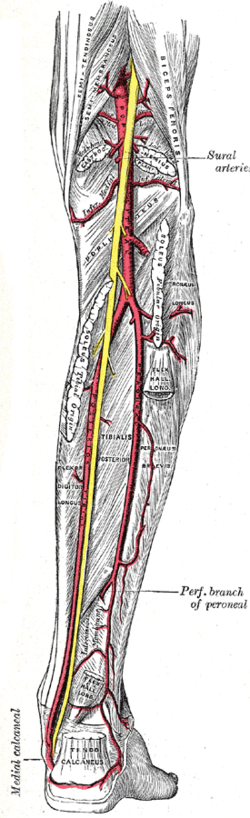
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

The popliteal vein is a vein of the lower limb. It is formed from the anterior tibial vein and the posterior tibial vein. It travels medial to the popliteal artery, and becomes the femoral vein. It drains blood from the leg. It can be assessed using medical ultrasound. It can be affected by popliteal vein entrapment.

In anatomy, the fibular veins are accompanying veins of the fibular artery.
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb is an artery that carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It branches from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk.
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

The popliteal fossa is a shallow depression located at the back of the knee joint. The bones of the popliteal fossa are the femur and the tibia. Like other flexion surfaces of large joints, it is an area where blood vessels and nerves pass relatively superficially, and with an increased number of lymph nodes.
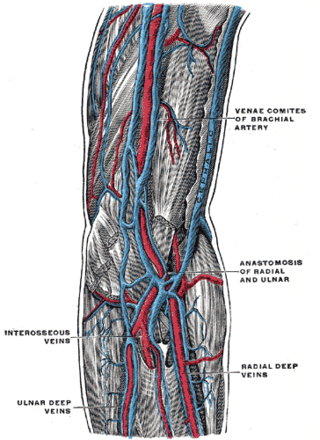
Vena comitans is Latin for accompanying vein and is also known as a satellite vein. It refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes.

The circumflex branch of left coronary artery is a branch of the left coronary artery. It winds around the left side of the heart along the atrioventricular groove. It supplies the posterolateral portion of the left ventricle.
Circumflex artery may refer to:

The posterior humeral circumflex artery arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the distal border of the subscapularis.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:
The posterior tibial recurrent artery, an inconstant branch, is given off from the anterior tibial before that vessel passes through the gap between superior tibio-fibular joint and upper border of interosseous membrane.
Tibiofibular trunk is an arterial trunk representing the direct continuation of the popliteal artery distal to where the anterior tibial artery branches off from it. The tibiofibular trunk terminates by bifurcating into two terminal branches: the posterior tibial artery, and the fibular artery. This is the most common configuration of the origins of these arteries, however, many other anatomical variations exist.

The anterior compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles that produce dorsiflexion and participate in inversion and eversion of the foot, as well as vascular and nervous elements, including the anterior tibial artery and veins and the deep fibular nerve.

The posterior compartment of the thigh is one of the fascial compartments that contains the knee flexors and hip extensors known as the hamstring muscles, as well as vascular and nervous elements, particularly the sciatic nerve.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk.