In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

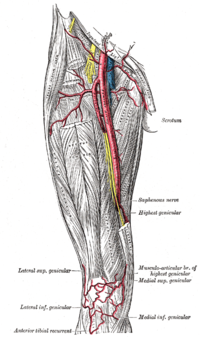
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
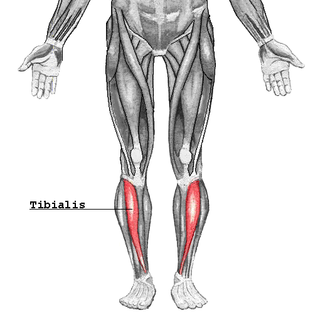
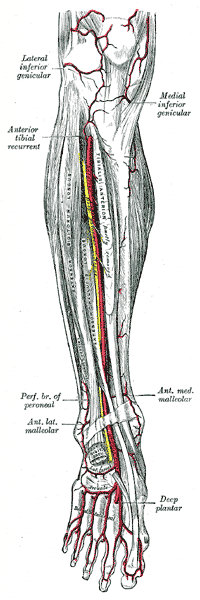
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The superior genicular arteries, two in number, arise one on either side of the popliteal artery, and wind around the femur immediately above its condyles to the front of the knee-joint. The medial superior genicular artery is on the inside of the knee and the lateral superior genicular artery is on the outside.

The lateral superior genicular artery is a branch of the popliteal artery that supplies a portion of the knee joint.

The medial superior genicular artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It runs deep to the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and tendon of the adductor magnus, and superior to the medial head of the gastrocnemius.

The inferior genicular arteries, two in number, arise from the popliteal beneath the gastrocnemius. On the inside of the knee, is the medial inferior genicular artery, and on the outer side is the lateral inferior genicular artery.

The lateral inferior genicular is an artery of the leg.

The lateral circumflex femoral artery is an artery in the upper thigh. It is usually a branch of the profunda femoris artery, and produces three branches. It is mostly distributed to the muscles of the lateral thigh, supplying arterial blood to muscles of the knee extensor group.
The cruciate anastomosis is a circulatory anastomosis in the upper thigh formed by the inferior gluteal artery, the lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries, the first perforating artery of the deep femoral artery, and the anastomotic branch of the posterior branch of the obturator artery.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The descending genicular artery arises from the femoral artery just before its passage through the adductor hiatus.
The sural arteries are two large branches, lateral and medial, which are distributed to the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles. Sural means related to the calf. The term applies to any of four or five arteries arising from the popliteal artery, with distribution to the muscles and integument of the calf, and with anastomoses to the posterior tibial, medial and lateral inferior genicular arteries.

The patellar network is an intricate network of blood vessels around and above the patella, and on the contiguous ends of the femur and tibia, forming a superficial and a deep plexus.

The genicular arteries are six arteries in the human leg, five of which are branches of the popliteal artery, that anastomose in the knee region in the patellar network or genicular anastomosis. They supply blood to the patella, together with contributions from the descending genicular artery, anterior tibial recurrent artery, and descending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery.