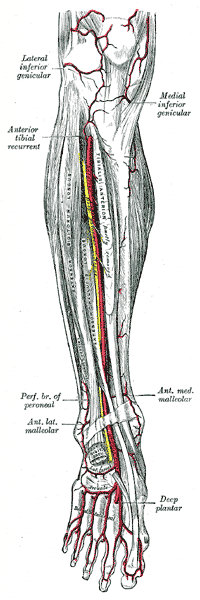
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space. It carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.

The transverse cervical artery is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery.
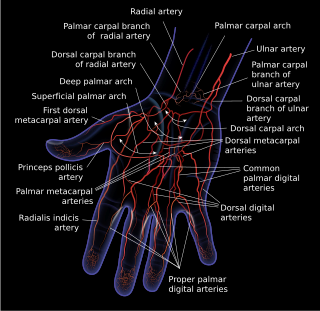
The superficial palmar arch is formed predominantly by the ulnar artery, with a contribution from the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery. However, in some individuals the contribution from the radial artery might be absent, and instead anastomoses with either the princeps pollicis artery, the radialis indicis artery, or the median artery, the former two of which are branches from the radial artery.

The superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third. It is a sensory nerve.

The scapular anastomosis is a system connecting certain subclavian artery and their corresponding axillary artery, forming a circulatory anastomosis around the scapula. It allows blood to flow past the joint in case of occlusion, damage, or pinching of the following scapular arteries:

The radialis indicis artery is a branch of the radial artery that provides blood to the index finger.

The plantar metatarsal arteries are four in number, arising from the convexity of the plantar arch. They run forward between the metatarsal bones and in contact with the Interossei. They are located in the fourth layer of the foot.

The medial plantar artery, much smaller than the lateral plantar artery, passes forward along the medial side of the foot.

The dorsal artery of the penis is an artery on the top surface of the penis. It is a branch of the internal pudendal artery. It runs forward on the dorsum of the penis to the glans, where it divides into two branches to the glans penis and the foreskin (prepuce).

Most of the dorsal metacarpal arteries arise from the dorsal carpal arch and run downward on the second, third, and fourth dorsal interossei of the hand and bifurcate into the dorsal digital arteries. Near their origin, they anastomose with the deep palmar arch by perforating arteries. They also anastomose with common palmar digital arteries, also via perforating arteries.

The proper palmar digital arteries travel along the sides of the phalanges, each artery lying just below its corresponding digital nerve.
The arcuate artery of the foot gives off the second, third, and fourth dorsal metatarsal arteries, which run forward upon the corresponding Interossei dorsales; in the clefts between the toes, each divides into two dorsal digital branches for the adjoining toes.

Dorsal digital nerves of radial nerve are branches on the dorsum of the hand.

Dorsal digital nerves of ulnar nerve are branches on the dorsum of the hand. The dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve divides into two dorsal digital branches; one supplies the ulnar side of the little finger; the other, the adjacent sides of the little and ring fingers. It also sends a twig to join that given by the superficial branch of the radial nerve for the adjoining sides of the middle and ring fingers, and assists in supplying them.

The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
Dorsal artery may refer to:
Digital arteries are arteries that relate to fingers and toes.

Dorsal digital arteries arise from the bifurcation of dorsal metacarpal arteries. They travel along the sides and dorsal aspects of the phalanges of the middle finger, ring finger, and little finger. They communicate with the proper palmar digital arteries.
Dorsal digital arteries may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.