| Arcuate artery of the foot | |
|---|---|
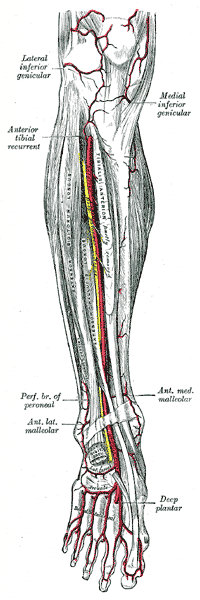 Anterior tibial artery, dorsalis pedis artery and the muscles and bones of the leg seen from the front (arcuate arteries very faintly labeled at bottom center) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Arteria dorsalis pedis |
| Branches | Dorsal metatarsal arteries |
| Vein | Dorsal venous arch of the foot |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria arcuata pedis |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.051 |
| TA2 | 4717 |
| FMA | 44594 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The arcuate artery of the foot (metatarsal artery) arises from dorsalis pedis slightly anterior to the lateral tarsal artery, specifically over the naviculocuneiform joint; it passes lateralward, over the bases of the lateral four metatarsal bones, beneath the tendons of the extensor digitorum brevis, its direction being influenced by its point of origin; and it terminates in the lateral tarsal artery. It communicates with the plantar arteries through the perforating arteries of the foot.
It runs with the lateral terminal branch of deep fibular nerve. This vessel gives off the second, third, and fourth dorsal metatarsal arteries.
It is not present in all individuals. [1]