
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space. It carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei of the foot are four muscles situated between the metatarsal bones.

The superficial fibular nerve is a mixed nerve that provides motor innervation to the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles, and sensory innervation to skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.
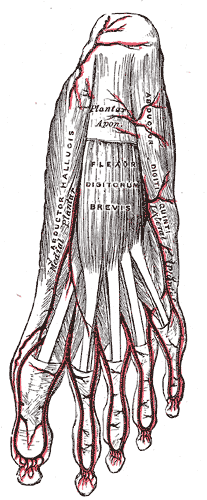
The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.

The superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third. It is a sensory nerve.

The medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.

The lateral plantar artery, much larger than the medial, passes obliquely lateralward and forward to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.

The plantar metatarsal arteries are four in number, arising from the convexity of the plantar arch. They run forward between the metatarsal bones and in contact with the Interossei. They are located in the fourth layer of the foot.

The deep plantar artery descends into the sole of the foot, between the two heads of the 1st interosseous dorsalis, and unites with the termination of the lateral plantar artery, to complete the plantar arch.

The plantar arch is a circulatory anastomosis formed from:
The first dorsal metatarsal artery is a small artery on the back of the foot. It runs forward on the first interosseous dorsalis muscle, and at the cleft between the great and second toes divides into two branches, one of which passes beneath the tendon of the extensor hallucis longus muscle, and is distributed to the medial border of the great toe; the other bifurcates to supply the adjoining sides of the great and second toes.
The arcuate artery of the foot gives off the second, third, and fourth dorsal metatarsal arteries, which run forward upon the corresponding Interossei dorsales; in the clefts between the toes, each divides into two dorsal digital branches for the adjoining toes.

The superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into a proper and a common plantar digital nerve:

Dorsal digital nerves of foot are branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, sural nerve and deep fibular nerve.

The proper plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot that arise from the superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve. The superficial branch splits into a proper digital nerve and a common digital nerve:

The proper plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. They primarily arise from the medial plantar nerve's superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch of the medial plantar nerve turns into a proper digital nerve and is responsible for supplies the medial side of the great toe.












