This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

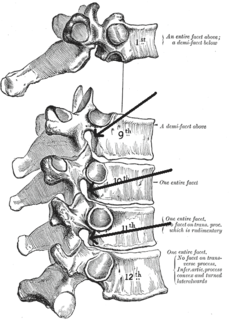
The lumbar vertebrae are, in human anatomy, the five vertebrae between the rib cage and the pelvis. They are the largest segments of the vertebral column and are characterized by the absence of the foramen transversarium within the transverse process and by the absence of facets on the sides of the body. They are designated L1 to L5, starting at the top. The lumbar vertebrae help support the weight of the body, and permit movement.

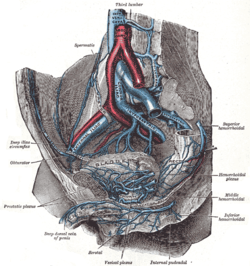
The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery, often abbreviated as IMA, is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the left colic flexure to the upper part of the rectum, which includes the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum. Proximally, its territory of distribution overlaps with the middle colic artery, and therefore the superior mesenteric artery. The SMA and IMA anastomose via the marginal artery of the colon and via Riolan's arcade. The territory of distribution of the IMA is more or less equivalent to the embryonic hindgut.

The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the psoas major muscles. They exit the pelvic girdle posterior and inferior to the inguinal ligament about one third laterally from the insertion point of the inguinal ligament on the pubic tubercle at which point they are referred to as the femoral arteries. The external iliac artery is usually the artery used to attach the renal artery to the recipient of a kidney transplant.

The common iliac arteries are two large arteries that originate from the aortic bifurcation at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra. They end in front of the sacroiliac joint, one on either side, and each bifurcates into the external and internal iliac arteries.
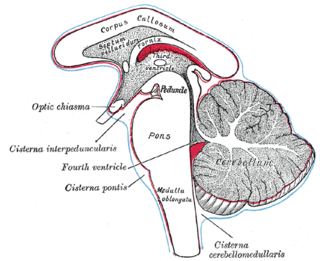
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space separates two of the meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.

In human anatomy, the anterior spinal artery is the artery that supplies the anterior portion of the spinal cord. It arises from branches of the vertebral arteries and courses along the anterior aspect of the spinal cord. It is reinforced by several contributory arteries, especially the artery of Adamkiewicz.

The external oblique muscle is the largest and the outermost of the three flat muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.
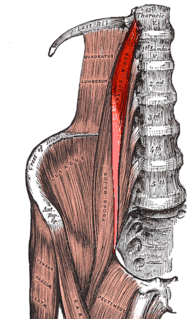
The psoas minor is a long, slender skeletal muscle which, when present, is located anterior to the psoas major muscle.

The conus medullaris or conus terminalis is the tapered, lower end of the spinal cord. It occurs near lumbar vertebral levels 1 (L1) and 2 (L2), occasionally lower. The upper end of the conus medullaris is usually not well defined.

In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar vertebrae and sacral vertebrae (L4-S4). A sacral plexopathy is a disorder affecting the nerves of the sacral plexus, usually caused by trauma, nerve compression, vascular disease, or infection. Symptoms may include pain, loss of motor control, and sensory deficits.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.
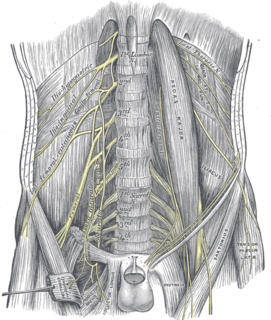
The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.

The median sacral artery is a small vessel that arises posterior to the abdominal aorta and superior to its bifurcation.

The lumbar arteries are arteries located in the lower back or lumbar region. The lumbar arteries are in parallel with the intercostals.

The anterior division of the twelfth thoracic nerve is larger than the others; it runs along the lower border of the twelfth rib, often gives a communicating branch to the first lumbar nerve, and passes under the lateral lumbocostal arch.
The subcostal arteries, so named because they lie below the last ribs, constitute the lowest pair of branches derived from the thoracic aorta, and are in series with the intercostal arteries.

The deep circumflex iliac artery is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone.