The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body. The word cecum stems from the Latin caecus meaning blind.

The ileum is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.
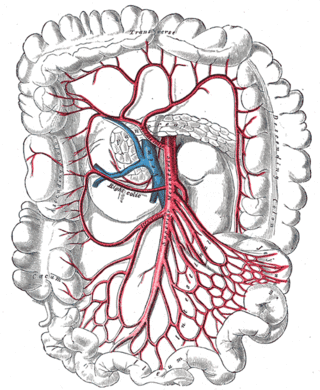
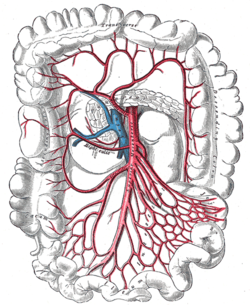
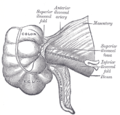
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

In human anatomy, the marginal artery of the colon, also known as the marginal artery of Drummond, the artery of Drummond, and simply as the marginal artery, is an artery that connects the inferior mesenteric artery with the superior mesenteric artery. It is sometimes absent, as an anatomical variant.

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.

The sigmoid arteries are 2–5 branches of the inferior mesenteric artery that are distributed to the distal descending colon and the sigmoid colon.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The middle colic artery is an artery of the abdomen; a branch of the superior mesenteric artery distributed to parts of the ascending and transverse colon. It usually divides into two terminal branches - a left one and a right one - which go on to form anastomoses with the left colic artery, and right colic artery (respectively), thus participating in the formation of the marginal artery of the colon.

The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively).

The anterior cecal artery is a branch of the ileocolic artery which supplies the anterior region of the cecum.

The posterior cecal artery is a branch of the ileocolic artery.

The appendicular artery, also known as the appendiceal artery, commonly arises from the terminal branch of the ileocolic artery, or less commonly from the posterior cecal artery or an ileal artery. It descends behind the termination of the ileum and enters the mesoappendix of the vermiform appendix. It runs near the free margin of the mesoappendix and ends in branches which supply the appendix.

The testicular artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles.
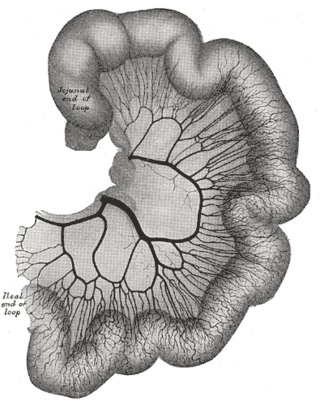
The arterial arcades are a series of anastomosing arterial arches between the arterial branches of the jejunum and ileum.

The ileocecal fold is an anatomical structure of the human abdomen formed by a layer of peritoneum between the ileum and cecum. The upper border of the ileocecal fold is fixed to the ileum opposite its mesenteric attachment, and the lower border passes over the ileocecal junction to join the mesentery of the appendix. Behind the ileocecal fold is the inferior ileocecal fossa.

The colic branch of ileocolic artery is a small artery in the abdomen. The ileocolic artery of the superior mesenteric artery branches off into the ascending colic artery, the anterior and posterior cecal arteries, the appendicular artery, and the ileal branches.

The superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups: