The human leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.
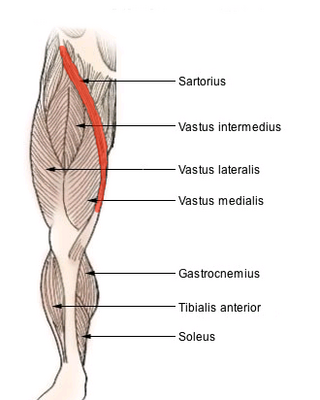
The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that runs down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment.

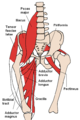
The quadriceps femoris muscle is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large fleshy mass which covers the front and sides of the femur. The name derives from Latin four-headed muscle of the femur.

In human anatomy, the groin is the junctional area between the abdomen and the thigh on either side of the pubic bone. This is also known as the medial compartment of the thigh that consists of the adductor muscles of the hip or the groin muscles.

The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.
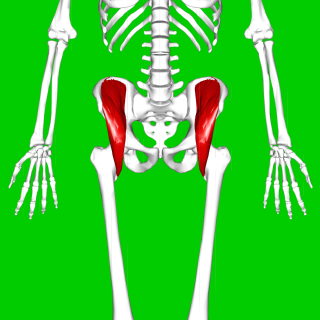
The iliacus is a flat, triangular muscle which fills the iliac fossa. It forms the lateral portion of iliopsoas, providing flexion of the thigh and lower limb at the acetabulofemoral joint.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.

The anterior superior iliac spine is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, and the sartorius muscle. The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior anterior iliac spine, and also about 5 cm away at the iliac tubercle.

The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus.

The iliohypogastric nerve is a nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus that supplies sensation to skin over the lateral gluteal and hypogastric regions and motor to the internal oblique muscles and transverse abdominal muscles.

The superior gluteal artery is the largest and final branch of the internal iliac artery. It is the continuation of the posterior division of that vessel. It is a short artery which runs backward between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve. It divides into a superficial and a deep branch after passing out of the pelvis above the upper border of the piriformis muscle.

The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet. Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.

The arcuate line of the ilium is a smooth rounded border on the internal surface of the ilium. It is immediately inferior to the iliac fossa and Iliacus muscle.

The wing(ala)of ilium is the large expanded portion of the ilium, the bone which bounds the greater pelvis laterally. It presents for examination two surfaces—an external and an internal—a crest, and two borders—an anterior and a posterior.
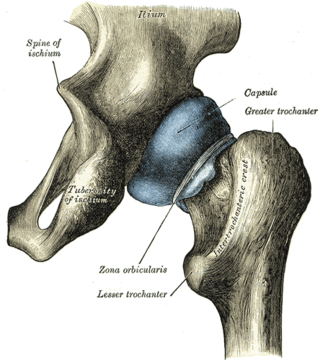
The ischial spine is part of the posterior border of the body of the ischium bone of the pelvis. It is a thin and pointed triangular eminence, more or less elongated in different subjects.

The crest of the ilium is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superiolateral margin of the greater pelvis.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The hip bone is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.