The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen is an opening or enclosed gap within the dense connective tissue of extant and extinct amniote animals, typically to allow passage of nerves, arteries, veins or other soft tissue structures from one body compartment to another.

The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia.

The piriformis muscle is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.

The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.
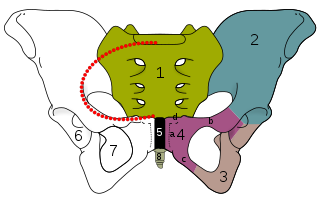
The obturator foramen is the large, bilaterally paired opening of the bony pelvis. It is formed by the pubis and ischium. It is mostly closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening, the obturator canal, through which the obturator nerve and vessels pass.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

The ischium forms the lower and back region of the hip bone.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body.
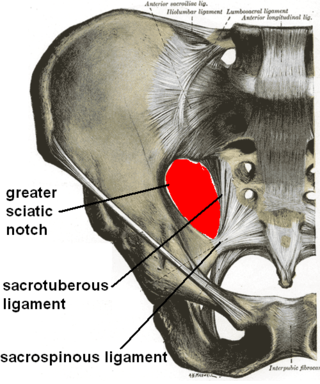
The sacrospinous ligament is a thin, triangular ligament in the human pelvis. The base of the ligament is attached to the outer edge of the sacrum and coccyx, and the tip of the ligament attaches to the spine of the ischium, a bony protuberance on the human pelvis. Its fibres are intermingled with the sacrotuberous ligament.

The inferior gluteal artery is a terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It is distributed chiefly to the buttock and the back of the thigh.

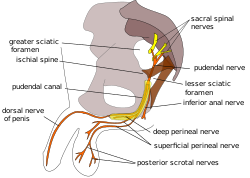
The lesser sciatic foramen is an opening between the pelvis and the back of the thigh. The foramen is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial tuberosity and the sacrospinous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial spine.

The pudendal canal is an anatomical structure formed by the obturator fascia lining the lateral wall of the ischioanal fossa. The internal pudendal artery and veins, and pudendal nerve pass through the pudendal canal, and the perineal nerve arises within it.

The nerve to obturator internus is a mixed nerve providing motor innervation to the obturator internus muscle and gemellus superior muscle, and sensory innervation to the hip joint. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It is one of the group of deep gluteal nerves.

The nerve to quadratus femoris is a nerve of the sacral plexus that provides motor innervation to the quadratus femoris muscle and gemellus inferior muscle, and an articular branch to the hip joint. The nerve leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen.

The greater sciatic notch is a notch in the ilium, one of the bones that make up the human pelvis. It lies between the posterior inferior iliac spine (above), and the ischial spine (below). The sacrospinous ligament changes this notch into an opening, the greater sciatic foramen.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The hip bone is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.

The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hip that rotate the femur in the hip joint.