
The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore, the radius is considered to be the larger of the two.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior (front) part of the upper and medial (inner) aspect of the thigh. The pectineus muscle is the most anterior adductor of the hip. The muscle does adduct and internally rotate the thigh but its primary function is hip flexion.

The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located in the lateral lumbar region between the vertebral column and the brim of the lesser pelvis. It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas. In animals, this muscle is equivalent to the tenderloin.

The psoas minor muscle is a long, slender skeletal muscle. When present, it is located anterior to the psoas major muscle.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.

In vertebrates, the pubic region is the most forward-facing of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body.
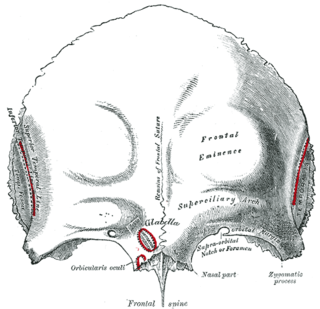
The squamous part of the frontal bone is the superior portion when viewed in standard anatomical orientation. There are two surfaces of the squamous part of the frontal bone: the external surface, and the internal surface.

The arcuate line of the ilium is a smooth rounded border on the internal surface of the ilium. It is immediately inferior to the iliac fossa and Iliacus muscle.
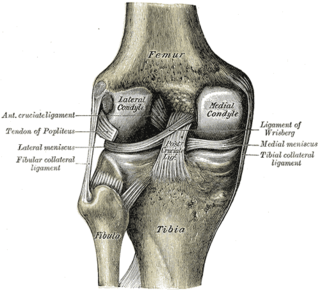
The lower extremity of femur is the lower end of the femur in human and other animals, closer to the knee. It is larger than the upper extremity of femur, is somewhat cuboid in form, but its transverse diameter is greater than its antero-posterior; it consists of two oblong eminences known as the lateral condyle and medial condyle.

The wing(ala)of ilium is the large expanded portion of the ilium, the bone which bounds the greater pelvis laterally. It presents for examination two surfaces—an external and an internal—a crest, and two borders—an anterior and a posterior.

The iliac fascia, or Abernethy's fascia, is a fascia in the region of the ilium of the pelvis.
The iliopectineal line is the border of the iliopubic eminence. It can be defined as a compound structure of the arcuate line and pectineal line. With the sacral promontory, it makes up the linea terminalis.
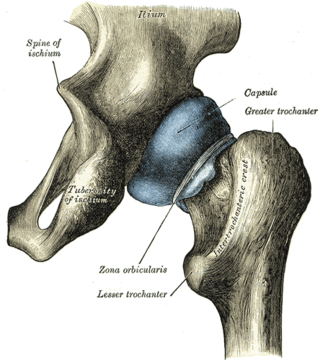
The articular capsule is strong and dense.
The Iliopectineal arch is a thickened band of fused iliac fascia and psoas fascia passing from the posterior aspect of the inguinal ligament anteriorly across the front of the femoral nerve to attach to the iliopubic eminence of the hip bone posteriorly. The iliopectineal arch thus forms a septum which subdivides the space deep to the inguinal ligament into a lateral muscular lacuna and a medial vascular lacuna. When a psoas minor muscle is present, its tendon of insertion blends with the iliopectineal arch

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

The iliopectineal bursa or the iliopsoas bursa is a large synovial bursa that separates the external surface of the hip joint capsule from the normally just the tendon of the iliopsoas muscle.





















